Differential role of SIRT1/MAPK pathway during cerebral ischemia in rats and humans
- PMID: 33737560
- PMCID: PMC7973546
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-85577-9
Differential role of SIRT1/MAPK pathway during cerebral ischemia in rats and humans
Abstract
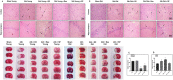
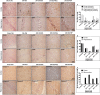
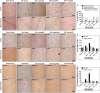
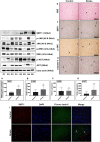
Cerebral ischemia (CI) is a severe cause of neurological dysfunction and mortality. Sirtuin-1 (Silent information regulator family protein 1, SIRT1), an oxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)-dependent protein deacetylase, plays an important role in protection against several neurodegenerative disorders. The present study aims to investigate the protective role of SIRT1 after CI in experimental young and aged rats and humans. Also, the study examines the possible regulatory mechanisms of neuronal death in CI settings. Immunoblotting and immunohistochemistry were used to evaluate changes in the expression of SIRT1, JNK/ERK/MAPK/AKT signaling, and pro-apoptotic caspase-3 in experimental rats and CI patients. The study findings demonstrated that, in aged experimental rats, SIRT1 activation positively influenced JNK and ERK phosphorylation and modulated neuronal survival in AKT-dependent manner. Further, the protection conferred by SIRT1 was effectively reversed by JNK inhibition and increased pro-apoptotic caspase-3 expression. In young experimental rats, SIRT1 activation decreased the phosphorylation of stress-induced JNK, ERK, caspase-3, and increased the phosphorylation of AKT after CI. Inhibition of SIRT1 reversed the protective effect of resveratrol. More importantly, in human patients, SIRT1 expression, phosphorylation of JNK/ERK/MAPK/AKT signaling and caspase-3 were up-regulated. In conclusion, SIRT1 could possibly be involved in the modulation of JNK/ERK/MAPK/AKT signaling pathway in experimental rats and humans after CI.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
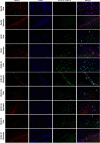
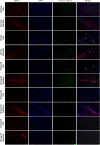
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

