Serial lung ultrasounds in pediatric pneumonia in Mozambique and Pakistan
- PMID: 33737572
- PMCID: PMC7973793
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-85485-y
Serial lung ultrasounds in pediatric pneumonia in Mozambique and Pakistan
Abstract
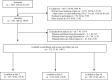
Lung ultrasound (LUS) is a promising point-of-care imaging technology for diagnosing and managing pneumonia. We sought to explore serial LUS examinations in children with chest-indrawing pneumonia in resource-constrained settings and compare their clinical and LUS imaging courses longitudinally. We conducted a prospective, observational study among children aged 2 through 23 months with World Health Organization Integrated Management of Childhood Illness chest-indrawing pneumonia and among children without fast breathing, chest indrawing or fever (no pneumonia cohort) at 2 district hospitals in Mozambique and Pakistan. We assessed serial LUS at enrollment, 2, 6, and 14 days, and performed a secondary analysis of enrolled children's longitudinal clinical and imaging courses. By Day 14, the majority of children with chest-indrawing pneumonia and consolidation on enrollment LUS showed improvement on follow-up LUS (100% in Mozambique, 85.4% in Pakistan) and were clinically cured (100% in Mozambique, 78.0% in Pakistan). In our cohort of children with chest-indrawing pneumonia, LUS imaging often reflected the clinical course; however, it is unclear how serial LUS would inform the routine management of non-severe chest-indrawing pneumonia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical