Gene Set Index Based on Different Modules May Help Differentiate the Mechanisms of Alzheimer's Disease and Vascular Dementia
- PMID: 33737807
- PMCID: PMC7961151
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S297483
Gene Set Index Based on Different Modules May Help Differentiate the Mechanisms of Alzheimer's Disease and Vascular Dementia
Abstract
Purpose: Alzheimer's disease (AD) and vascular dementia shared similar symptoms, the aim of the present study was to identify potential differences in the mechanisms underlying the two diseases.
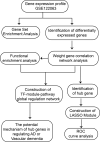
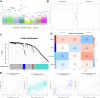
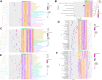
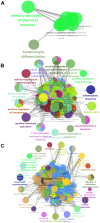
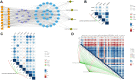
Materials and methods: The data set including AD, vascular dementia, and control samples was carried out gene differential expression analysis, weighted gene co-expression network analysis, functional enrichment, protein-protein interaction network construction, and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator analysis to reveal the differences in the mechanisms underlying the two diseases and potential diagnostic gene signature.
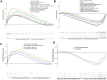
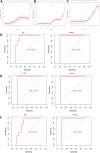
Results: We identified the gene modules related to AD or vascular dementia. Enrichment analysis of module genes and construction of a protein-protein interaction network suggested that the "brown" module may be involved in a chemokine pathway, the "blue" module may be involved in cortisol synthesis and secretion, and the "turquoise" module may be involved in cholinergic synapse transmission. The hub gene-based signature index may be a biomarker of AD and vascular dementia and may even differentiate the two diseases from each other with high area under curve.
Conclusion: Our results identified not only core pathways involved in both AD and vascular disease, but also their potentially specific pathways. We proposed the hub gene-based signature index may be useful for diagnosing AD and vascular dementia.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; LASSO; WGCNA; vascular dementia; weighted gene co-expression network analysis.
© 2021 Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that this research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Jian C, Lu M, Zhang Z, et al. miR-34a knockout attenuates cognitive deficits in APP/PS1 mice through inhibition of the amyloidogenic processing of APP. Life Sci. 2017;182:104–111. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

