Adaptive Rewiring in Weighted Networks Shows Specificity, Robustness, and Flexibility
- PMID: 33737871
- PMCID: PMC7960922
- DOI: 10.3389/fnsys.2021.580569
Adaptive Rewiring in Weighted Networks Shows Specificity, Robustness, and Flexibility
Abstract
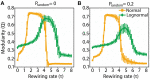
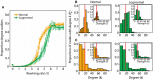
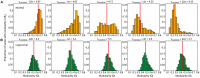
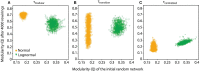
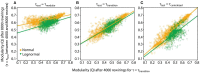
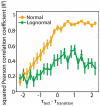
Brain network connections rewire adaptively in response to neural activity. Adaptive rewiring may be understood as a process which, at its every step, is aimed at optimizing the efficiency of signal diffusion. In evolving model networks, this amounts to creating shortcut connections in regions with high diffusion and pruning where diffusion is low. Adaptive rewiring leads over time to topologies akin to brain anatomy: small worlds with rich club and modular or centralized structures. We continue our investigation of adaptive rewiring by focusing on three desiderata: specificity of evolving model network architectures, robustness of dynamically maintained architectures, and flexibility of network evolution to stochastically deviate from specificity and robustness. Our adaptive rewiring model simulations show that specificity and robustness characterize alternative modes of network operation, controlled by a single parameter, the rewiring interval. Small control parameter shifts across a critical transition zone allow switching between the two modes. Adaptive rewiring exhibits greater flexibility for skewed, lognormal connection weight distributions than for normally distributed ones. The results qualify adaptive rewiring as a key principle of self-organized complexity in network architectures, in particular of those that characterize the variety of functional architectures in the brain.
Keywords: evolving network model; functional connectivity; hebbian plasticity; network diffusion; robustness; specificity; structural plasticity; structure function relation.
Copyright © 2021 Rentzeperis and van Leeuwen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

