Off-label use of intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke: a critical appraisal of randomized and real-world evidence
- PMID: 33737956
- PMCID: PMC7934037
- DOI: 10.1177/1756286421997368
Off-label use of intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke: a critical appraisal of randomized and real-world evidence
Abstract
Intravenous thrombolysis (IVT) represents the only systemic reperfusion therapy able to reverse neurological deficit in patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS). Despite its effectiveness in patients with or without large vessel occlusion, it can be offered only to a minority of them, because of the short therapeutic window and additional contraindications derived from stringent but arbitrary inclusion and exclusion criteria used in landmark randomized controlled clinical trials. Many absolute or relative contraindications lead to disparities between the official drug label and guidelines or expert recommendations. Based on recent advances in neuroimaging and evidence from cohort studies, off-label use of IVT is increasingly incorporated into the daily practice of many stroke centers. They relate to extension of therapeutic time windows, and expansion of indications in co-existing conditions originally listed in exclusion criteria, such as use of alternative thrombolytic agents, pre-treatment with antiplatelets, anticoagulants or low molecular weight heparins. In this narrative review, we summarize recent randomized and real-world data on the safety and efficacy of off-label use of IVT for AIS. We also make some practical recommendations to stroke physicians regarding the off-label use of thrombolytic agents in complex and uncommon presentations of AIS or other conditions mimicking acute cerebral ischemia. Finally, we provide guidance on the risks and benefits of IVT in numerous AIS subgroups, where equipoise exists and guidelines and treatment practices vary.
Keywords: alteplase; contraindications; intracranial bleeding; intravenous thrombolysis; ischemic stroke; large vessel occlusion; off-label; tenecteplase; therapeutic window.
© The Author(s), 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


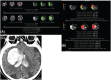

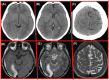



References
-
- Tsivgoulis G, Kargiotis O, Alexandrov AV. Intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke: a bridge between two centuries. Expert Rev Neurother 2017; 17: 819–837. - PubMed
-
- Tsivgoulis G, Lioutas VA. Real-world evidence for off-label intravenous thrombolysis in acute ischaemic stroke. Eur J Neurol 2018; 25: 213–214. - PubMed
-
- Martins SCO, Weiss G, Almeida AG, et al. Validation of a smartphone application in the evaluation and treatment of acute stroke in a comprehensive stroke center. Stroke 2020; 51: 240–246. - PubMed
-
- Feda S, Nikoubashman O, Schürmann K, et al. Endovascular stroke treatment does not preclude high thrombolysis rates. Eur J Neurol 2019; 26: 428–e33. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

