Bestrophinopathies: perspectives on clinical disease, Bestrophin-1 function and developing therapies
- PMID: 33738427
- PMCID: PMC7934022
- DOI: 10.1177/2515841421997191
Bestrophinopathies: perspectives on clinical disease, Bestrophin-1 function and developing therapies
Abstract
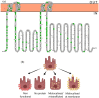
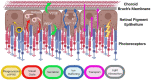
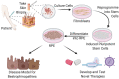
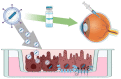
Bestrophinopathies are a group of clinically distinct inherited retinal dystrophies that typically affect the macular region, an area synonymous with central high acuity vision. This spectrum of disorders is caused by mutations in bestrophin1 (BEST1), a protein thought to act as a Ca2+-activated Cl- channel in the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) of the eye. Although bestrophinopathies are rare, over 250 individual pathological mutations have been identified in the BEST1 gene, with many reported to have various clinical expressivity and incomplete penetrance. With no current clinical treatments available for patients with bestrophinopathies, understanding the role of BEST1 in cells and the pathological pathways underlying disease has become a priority. Induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) technology is helping to uncover disease mechanisms and develop treatments for RPE diseases, like bestrophinopathies. Here, we provide a comprehensive review of the pathophysiology of bestrophinopathies and highlight how patient-derived iPSC-RPE are being used to test new genomic therapies in vitro.
Keywords: BEST1; CRISPR; bestrophinopathies; gene editing; gene therapy; induced pluripotent stem cells.
© The Author(s), 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Leroy BP. Bestrophinopathies. In: Traboulsi EI. (ed.) Genetic diseases of the eye. 2nd ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2012, pp. 426–436.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

