Tiletamine/zolazepam and dexmedetomidine with tramadol provide effective general anesthesia in rats
- PMID: 33738435
- PMCID: PMC7954827
- DOI: 10.1002/ame2.12143
Tiletamine/zolazepam and dexmedetomidine with tramadol provide effective general anesthesia in rats
Abstract
Background: Tiletamine/zolazepam is a dissociative anesthetic combination commonly used in small animals but information is limited in rats. The alpha-2 agonist, dexmedetomidine, has gained popularity in laboratory animal anesthesia. Tramadol is a weak opioid mu agonist. The aim of this study was to assess whether the tiletamine/zolazepam/dexmedetomidine (ZD) combination effectively provides a surgical anesthesia plane comparable to tiletamine/zolazepam/dexmedetomidine with tramadol (ZDT) in a minor procedure in rats.
Methods: Rats were induced with ZD or ZDT. After the loss of paw withdrawal, a small incision was made on the rats' left thighs as a surgical stimulus. Rats were maintained under a surgical anesthesia plane by assessing the loss of the paw withdrawal reflex for 45 minutes, then atipamezole was administered. Monitored anesthesia parameters included: (a) physiological parameters - pulse rate (PR), respiratory rate (RR), tissue oxygen saturation (%SpO2), and body temperature; (b) duration parameters - induction time, onset and duration of surgical anesthesia plane, onset of recovery, and recovery time.
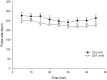
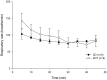
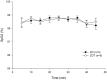
Results: PR was significantly lower at 10 minutes in ZD and 5 minutes in ZDT groups. No difference was observed for RR, %SpO2, and body temperature. Likewise, there were no differences for duration parameters: induction time was less than 3 minutes; onset and duration of surgical anesthesia plane were approximately 5 and 45 minutes, respectively; onset of recovery (time to move) was 51 minutes; and recovery time was 52 minutes, respectively.
Conclusion: These data suggest the ZD combination provides a surgical anesthesia plane comparable to ZDT in a rat incisional pain model.
Keywords: anesthesia; dexmedetomidine; rats; tiletamine; tramadol.
© 2021 The Authors. Animal Models and Experimental Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of The Chinese Association for Laboratory Animal Sciences.
Figures

References
-
- Pa F. Laboratory Animal Anesthesia. 2nd ed. London: Academic Press; 1996.
-
- Roberts F, Freshwater‐Turner D. Pharmacokinetics and anaesthesia. Continuing Educ Anaesthesia Crit Care Pain. 2007;7:25‐29.
-
- Fish R, Danneman P, Brown M, Karas A. Anesthesia and Analgesia in Laboratory Animals. 2nd ed. New York, NY: Academic Press; 2008.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

