Factors affecting time to brain metastases for stage 2 and 3 breast cancer patients: A large single-institutional analysis with potential screening implications
- PMID: 33738445
- PMCID: PMC7954098
- DOI: 10.1093/noajnl/vdab009
Factors affecting time to brain metastases for stage 2 and 3 breast cancer patients: A large single-institutional analysis with potential screening implications
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is the second most common cancer associated with brain metastases. The purpose of this study was to identify factors that impact the time to brain metastases in breast cancer patients at a single institution.
Methods: Single institution retrospective study that captured all consecutive stage 2 and stage 3 breast cancer patients from 2003 to 2010. Patient characteristics analyzed included age, hormone status, HER2 receptor status, grade, stage, and time from breast cancer diagnosis to brain metastasis.
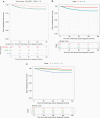
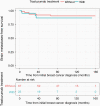
Results: A total of 1218 patients were eligible for the final analysis. 849 (69.7%) patients were ER+/HER2-, 90 (7.4%) were HER2+, and 279 (22.9%) were triple-negative (TN). Overall, 74 patients (6.1%) developed brain metastases over a median follow up time of 92 months. Median times to brain metastases for HER2+, TN, and ER+/HER2- patients were 20, 26, and 57 months, respectively. Multivariate analysis demonstrated that TN disease (HR = 2.043, P = .015), grade (HR = 1.667, P = .024) and stage (HR = 3.851, P < .001) were independent risk factors for earlier brain metastases. Median times to brain metastases were 34 and 52 months for stage 3 and 2 patients, and 30, 49, and 71 months for grade 3, 2, and 1 tumors, respectively.
Conclusions: This single-institutional case series demonstrates that TN breast cancer, higher stage, and higher histologic grade are associated with earlier brain metastases in multivariate analysis. Additional prospective studies are warranted to investigate the impact of brain metastases screening on survival outcome in this high-risk defined group.
Keywords: HER2+ breast cancer; MRI screening; brain metastases; breast cancer; triple negative.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press, the Society for Neuro-Oncology and the European Association of Neuro-Oncology.
Figures
References
-
- Lin NU, Bellon JR, Winer EP. CNS metastases in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(17):3608–3617. - PubMed
-
- Tsukada Y, Fouad A, Pickren JW, Lane WW. Central nervous system metastasis from breast carcinoma. Autopsy study. Cancer. 1983;52(12):2349–2354. - PubMed
-
- Phillips C, Jeffree R, Khasraw M. Management of breast cancer brain metastases: a practical review. Breast. 2017;31:90–98. - PubMed
-
- Pestalozzi BC, Zahrieh D, Price KN, et al. ; International Breast Cancer Study Group (IBCSG) . Identifying breast cancer patients at risk for Central Nervous System (CNS) metastases in trials of the International Breast Cancer Study Group (IBCSG). Ann Oncol. 2006;17(6):935–944. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
