Transfer learning-based ensemble support vector machine model for automated COVID-19 detection using lung computerized tomography scan data
- PMID: 33738639
- PMCID: PMC7972022
- DOI: 10.1007/s11517-020-02299-2
Transfer learning-based ensemble support vector machine model for automated COVID-19 detection using lung computerized tomography scan data
Abstract
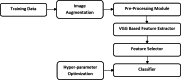
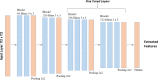
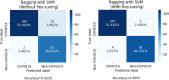
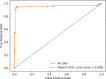
The novel discovered disease coronavirus popularly known as COVID-19 is caused due to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO). An early-stage detection of COVID-19 is crucial for the containment of the pandemic it has caused. In this study, a transfer learning-based COVID-19 screening technique is proposed. The motivation of this study is to design an automated system that can assist medical staff especially in areas where trained staff are outnumbered. The study investigates the potential of transfer learning-based models for automatically diagnosing diseases like COVID-19 to assist the medical force, especially in times of an outbreak. In the proposed work, a deep learning model, i.e., truncated VGG16 (Visual Geometry Group from Oxford) is implemented to screen COVID-19 CT scans. The VGG16 architecture is fine-tuned and used to extract features from CT scan images. Further principal component analysis (PCA) is used for feature selection. For the final classification, four different classifiers, namely deep convolutional neural network (DCNN), extreme learning machine (ELM), online sequential ELM, and bagging ensemble with support vector machine (SVM) are compared. The best performing classifier bagging ensemble with SVM within 385 ms achieved an accuracy of 95.7%, the precision of 95.8%, area under curve (AUC) of 0.958, and an F1 score of 95.3% on 208 test images. The results obtained on diverse datasets prove the superiority and robustness of the proposed work. A pre-processing technique has also been proposed for radiological data. The study further compares pre-trained CNN architectures and classification models against the proposed technique.
Keywords: COVID-19; CT scan data; Ensemble SVM; Transfer learning; VGG16.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

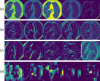
Similar articles
-
Optimised genetic algorithm-extreme learning machine approach for automatic COVID-19 detection.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 15;15(12):e0242899. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242899. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33320858 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Convolutional Neural Network-Based Computer-Aided Detection System for COVID-19 Using Multiple Lung Scans: Design and Implementation Study.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Apr 26;23(4):e27468. doi: 10.2196/27468. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 33848973 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Deep Learning and Ensemble Learning Mechanism for Delta-Type COVID-19 Detection.Front Public Health. 2022 Jul 8;10:875971. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.875971. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35874982 Free PMC article.
-
Development and integration of VGG and dense transfer-learning systems supported with diverse lung images for discovery of the Coronavirus identity.Inform Med Unlocked. 2022;32:101004. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2022.101004. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Inform Med Unlocked. 2022. PMID: 35822170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 diagnosis: A comprehensive review of pre-trained deep learning models based on feature extraction algorithm.Results Eng. 2023 Jun;18:101020. doi: 10.1016/j.rineng.2023.101020. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Results Eng. 2023. PMID: 36945336 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial intelligence-driven assessment of radiological images for COVID-19.Comput Biol Med. 2021 Sep;136:104665. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104665. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Comput Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 34343890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cloud-Based Quad Deep Ensemble Framework for the Detection of COVID-19 Omicron and Delta Variants.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Nov 9;13(22):3419. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13223419. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37998555 Free PMC article.
-
An Explainable AI-Enabled Framework for Interpreting Pulmonary Diseases from Chest Radiographs.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jan 3;15(1):314. doi: 10.3390/cancers15010314. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36612309 Free PMC article.
-
CNN-based transfer learning-BiLSTM network: A novel approach for COVID-19 infection detection.Appl Soft Comput. 2021 Jan;98:106912. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106912. Epub 2020 Nov 18. Appl Soft Comput. 2021. PMID: 33230395 Free PMC article.
-
LBP-based information assisted intelligent system for COVID-19 identification.Comput Biol Med. 2021 Jul;134:104453. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104453. Epub 2021 May 1. Comput Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 33957343 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WebMD Lung Diseases Overview (2020) https://www.webmd.com/lung/lung-diseases-overview#1, Last accessed date 22nd May
-
- Novel Coronavirus World Health Organization (WHO) (2020) https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019, Last accessed date 22nd May
-
- Worldometer Global COVID-19 Case Counter (2020) https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus, Last accessed date 22nd May
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

