Glycemic Variability and Time in Range During Self-titration of Once Daily Insulin Glargine 300 U/ml Versus Neutral Protamine Hagedorn Insulin in Insulin-naïve Chinese Type 2 Diabetes Patients
- PMID: 33738774
- PMCID: PMC8099948
- DOI: 10.1007/s13300-021-01046-6
Glycemic Variability and Time in Range During Self-titration of Once Daily Insulin Glargine 300 U/ml Versus Neutral Protamine Hagedorn Insulin in Insulin-naïve Chinese Type 2 Diabetes Patients
Abstract
Introduction: To compare glycemic variability (GV) and time in range (TIR) in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) initiated on once-daily bedtime insulin glargine 300U/ml (Gla-300) versus neutral protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM).
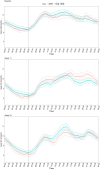
Methods: This was a 24-week, open-label exploratory study with 1:1 randomization comparing patient-adjusted titration of Gla-300 (n = 23) versus NPH (n = 23) at bedtime in insulin-naïve T2D patients on maximum oral glucose-lowering drugs. The starting dose was 0.2 U/kg/day and with self-titration of one unit per week to achieve a target fasting glucose of 4.4-6 mmol/l, without hypoglycemia. Participants had masked CGM at baseline, weeks 11 and 24. The primary outcome was between-treatment differences in CGM glucose standard deviation (SD) at week 24.
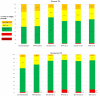
Results: HbA1c at week 24 were similar, with 21% of Gla-300 versus 4% of NPH-treated patients achieving HbA1c < 7% without confirmed hypoglycemia. There were no differences in anytime glucose SD at week 24 (LS mean difference - 0.08 mmol/l, 95% CI [- 0.42-0.26], p = 0.63). Anytime %TIRs (3.9-10.0 mmol/l) at week 24 were similar (p = 0.91). Nocturnal % time below range < 3.9 mmol/l was significantly lower in the Gla-300 group (least squares (LS) mean difference - 5.03% [- 9.92 to - 0.14], p = 0.04) with lower % coefficient of variation (LS mean difference - 4.5% [- 8.1 to - 0.8], p = 0.018). Diurnal TIR was higher in Gla-300 patients at week 11 but there were no differences at week 24.
Conclusions: Once-daily bedtime Gla-300 was associated with lower nocturnal GV, time below range and self-reported hypoglycemia in insulin-naïve Chinese T2D patients over a 24-week study period, as compared with NPH insulin.
Clinical trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03389490.
Keywords: Continuous glucose monitoring; Glucose variability; Insulin analogues.
Figures
References
-
- Porcellati F, Lucidi P, Candeloro P, et al. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and modulation of hepatic glucose production with insulin glargine U300 and glargine U100 at steady state with individualized clinical doses in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(1):85–92. doi: 10.2337/dc18-0706. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bolli GB, Riddle MC, Bergenstal RM, et al. New insulin glargine 300 U/ml compared with glargine 100 U/ml in insulin-naïve people with type 2 diabetes on oral glucose-lowering drugs: a randomized controlled trial (EDITION 3) Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015;17(4):386–394. doi: 10.1111/dom.12438. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bergenstal RM, Bailey TS, Rodbard D, et al. Comparison of insulin glargine 300 units/mL and 100 units/mL in adults with type 1 diabetes: continuous glucose monitoring profiles and variability using morning or evening injections. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(4):554–560. doi: 10.2337/dc16-0684. - DOI - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

