Yttrium-90 Radioembolization for the Treatment of Solitary, Unresectable HCC: The LEGACY Study
- PMID: 33739462
- PMCID: PMC8596669
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.31819
Yttrium-90 Radioembolization for the Treatment of Solitary, Unresectable HCC: The LEGACY Study
Abstract
Background and aims: Locoregional therapies, including yttrium-90 radioembolization, play an important role in the treatment of unresectable HCC. The aim of the LEGACY (Local radioEmbolization using Glass Microspheres for the Assessment of Tumor Control with Y-90) study was to evaluate objective response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DoR) in patients with solitary unresectable HCC treated with yttrium-90 glass microspheres.
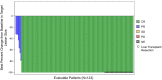
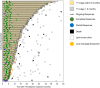
Approach and results: LEGACY is a multicenter, single-arm, retrospective study conducted at three sites that included all eligible, consecutive patients with HCC treated with radioembolization between 2014 and 2017. Eligibility criteria included solitary HCC ≤ 8 cm, Child-Pugh A cirrhosis, and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status 0-1. Primary endpoints were ORR and DoR based on modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors in the treated area (localized), as evaluated by blinded, independent, central review. Radioembolization was performed with intent of ablative-level dosimetry in a selective fashion when possible. Overall survival was evaluated using Kaplan-Meier and multivariate Cox proportional hazards. Among the 162 patients included, 60.5% were Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group 0, and the median tumor size was 2.7 cm (range: 1-8) according to blinded, independent, central review. Radioembolization served as neoadjuvant therapy for transplantation or resection in 21.0% (34 of 162) and 6.8% (11 of 162) of patients, respectively, and as primary treatment for all others. Median follow-up time was 29.9 months by reverse Kaplan-Meier. ORR (best response) was 88.3% (CI: 82.4-92.4), with 62.2% (CI: 54.1-69.8) exhibiting a DoR ≥ 6 months. Three-year overall survival was 86.6% for all patients and 92.8% for those neoadjuvant patients with resected or transplanted liver.
Conclusions: In this multicenter study of radioembolization, clinical meaningful response rates and prolonged DoR were observed in the treatment of unresectable, solitary HCC ≤ 8 cm.
© 2021 The Authors. Hepatology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures


References
-
- Galle PR, Forner A, Llovet JM, Mazzaferro V, Piscaglia F, Raoul JL, et al. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 2018;69:182‐236. - PubMed
-
- Lewandowski RJ, Gabr A, Abouchaleh N, Ali R, Al Asadi A, Mora RA, et al. Radiation segmentectomy: potential curative therapy for early hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology 2018;287:1050‐1058. - PubMed
-
- Padia SA, Kwan SW, Roudsari B, Monsky WL, Coveler A, Harris WP. Superselective yttrium‐90 radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma yields high response rates with minimal toxicity. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2014;25:1067‐1073. - PubMed
-
- Padia SA, Johnson GE, Horton KJ, Ingraham CR, Kogut MJ, Kwan S, et al. Segmental Yttrium‐90 radioembolization versus segmental chemoembolization for localized hepatocellular carcinoma: results of a single‐center, retrospective, propensity score‐matched study. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2017;28:777‐785.e771. - PubMed
-
- Biederman DM, Titano JJ, Korff RA, Fischman AM, Patel RS, Nowakowski FS, et al. Radiation segmentectomy versus selective chemoembolization in the treatment of early‐stage hepatocellular carcinoma. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2018;29:30‐37.e32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

