Beyond copy number: A new, rapid, and versatile method for sequencing the entire SMN2 gene in SMA patients
- PMID: 33739559
- PMCID: PMC8252042
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.24200
Beyond copy number: A new, rapid, and versatile method for sequencing the entire SMN2 gene in SMA patients
Abstract
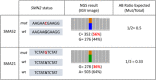
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is caused by bi-allelic loss or pathogenic variants in the SMN1 gene. SMN2, the highly homologous copy of SMN1, is considered the major phenotypic modifier of the disease. Determination of SMN2 copy number is essential to establish robust genotype-phenotype correlations and predict disease evolution, to stratify patients for clinical trials, as well as to define those eligible for treatment. Discordant genotype-phenotype correlations are not uncommon in SMA, some of which are due to intragenic SMN2 variants that may influence the amount of complete SMN transcripts and, therefore, of full-length SMN protein. Detection of these variants is crucial to predict SMA phenotypes in the present scenario of therapeutic advances and with the perspective of SMA neonatal screening and early diagnosis to start treatments. Here, we present a novel, affordable, and versatile method for complete sequencing of the SMN2 gene based on long-range polymerase chain reaction and next-generation sequencing. The method was validated by analyzing samples from 53 SMA patients who lack SMN1, allowing to characterize paralogous, rare variants, and single-nucleotide polymorphisms of SMN2 as well as SMN2-SMN1 hybrid genes. The method identifies partial deletions and can be adapted to determine rare pathogenic variants in patients with at least one SMN1 copy.
Keywords: SMN2 copies; next-generation sequencing; paralogous variants; phenotype-genotype correlations; spinal muscular atrophy.
© 2021 The Authors. Human Mutation published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
A patent is in preparation for this methodology and pipeline (I.C. and E. F. T.). E.F.T has received grant support to conduct clinical trials on SMA from Ionis/Biogen and serves as a consultant to AveXis, Novartis, Biogen, Biologix, Cytokinetics, Roche. The remaining authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures



References
-
- Alías, L. , Bernal, S. , Barceló, M. J. , Also‐Rallo, E. , Martínez‐Hernández, R. , Rodríguez‐Alvarez, F. J. , Hernández‐Chico, C. , Baiget, M. , & Tizzano, E. F. (2011). Accuracy of marker analysis, quantitative real‐time polymerase chain reaction, and multiple ligation‐dependent probe amplification to determine SMN2 copy number in patients with spinal muscular atrophy. Genetic Testing and Molecular Biomarkers, 15(9), 587–594. 10.1089/gtmb.2010.0253 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alías, L. , Bernal, S. , Fuentes‐Prior, P. , Barceló, M. J. , Also, E. , Martínez‐Hernández, R. , Rodríguez‐Alvarez, F. J. , Martín, Y. , Aller, E. , Grau, E. , Peciña, A. , Antiñolo, G. , Galán, E. , Rosa, A. L. , Fernández‐Burriel, M. , Borrego, S. , Millán, J. M. , Hernández‐Chico, C. , Baiget, M. , & Tizzano, E. F. (2009). Mutation update of spinal muscular atrophy in Spain: Molecular characterization of 745 unrelated patients and identification of four novel mutations in the SMN1 gene. Human Genetics, 125(1), 29–39. 10.1007/s00439-008-0598-1 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arkblad, E. L. , Darin, N. , Berg, K. , Kimber, E. , Brandberg, G. , Lindberg, C. , Holmberg, E. , Tulinius, M. , & Nordling, M. (2006). Multiplex ligation‐dependent probe amplification improves diagnostics in spinal muscular atrophy. Neuromuscular Disorders, 16(12), 830–838. 10.1016/j.nmd.2006.08.011 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bernal, S. , Alías, L. , Barceló, M. J. , Also‐Rallo, E. , Martínez‐Hernández, R. , Gámez, J. , Guillén‐Navarro, E. , Rosell, J. , Hernando, I. , Rodriguez‐Alvarez, F. J. , Borrego, S. , Millán, J. M. , Hernández‐Chico, C. , Baiget, M. , Fuentes‐Prior, P. , & Tizzano, E. F. (2010). The c.859>C variant in the SMN2 gene is associated with types II and III SMA and originates from a common ancestor. Journal of Medical Genetics, 47(9), 640–642. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

