Glofitamab, a Novel, Bivalent CD20-Targeting T-Cell-Engaging Bispecific Antibody, Induces Durable Complete Remissions in Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Lymphoma: A Phase I Trial
- PMID: 33739857
- PMCID: PMC8210975
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.20.03175
Glofitamab, a Novel, Bivalent CD20-Targeting T-Cell-Engaging Bispecific Antibody, Induces Durable Complete Remissions in Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Lymphoma: A Phase I Trial
Abstract
Purpose: Glofitamab is a T-cell-engaging bispecific antibody possessing a novel 2:1 structure with bivalency for CD20 on B cells and monovalency for CD3 on T cells. This phase I study evaluated glofitamab in relapsed or refractory (R/R) B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (B-NHL). Data for single-agent glofitamab, with obinutuzumab pretreatment (Gpt) to reduce toxicity, are presented.
Methods: Seven days before the first dose of glofitamab (0.005-30 mg), all patients received 1,000 mg Gpt. Dose-escalation steps were determined using a Bayesian continuous reassessment method with overdose control. Primary end points were safety, pharmacokinetics, and the maximum tolerated dose of glofitamab.
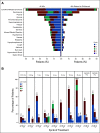
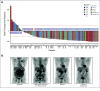
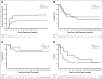
Results: Following initial single-patient cohorts, 171 patients were treated within conventional multipatient cohorts and received at least one dose of glofitamab. This trial included heavily pretreated patients with R/R B-NHL; most were refractory to prior therapy (155; 90.6%) and had received a median of three prior therapies. One hundred and twenty-seven patients (74.3%) had diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, transformed follicular lymphoma, or other aggressive histology, and the remainder had indolent lymphoma subtypes. Five (2.9%) patients withdrew from treatment because of adverse events. Cytokine release syndrome occurred in 86 of 171 (50.3%) patients (grade 3 or 4: 3.5%); two (1.2%) patients experienced grade 3, transient immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome-like symptoms. The overall response rate was 53.8% (complete response [CR], 36.8%) among all doses and 65.7% (CR, 57.1%) in those dosed at the recommended phase II dose. Of 63 patients with CR, 53 (84.1%) have ongoing CR with a maximum of 27.4 months observation.
Conclusion: In patients with predominantly refractory, aggressive B-NHL, glofitamab showed favorable activity with frequent and durable CRs and a predictable and manageable safety profile.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03075696.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Engaging results with glofitamab.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021 May;18(5):257. doi: 10.1038/s41571-021-00510-3. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33828233 No abstract available.
References
-
- International Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project : A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med 329:987-994, 1993 - PubMed
-
- Sehn LH Berry B Chhanabhai M, et al. : The revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) is a better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Blood 109:1857-1861, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

