Cardiac hypertrophy at autopsy
- PMID: 33740097
- PMCID: PMC8298245
- DOI: 10.1007/s00428-021-03038-0
Cardiac hypertrophy at autopsy
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Cardiac hypertrophy at autopsy.Virchows Arch. 2021 Jul;479(1):95. doi: 10.1007/s00428-021-03118-1. Virchows Arch. 2021. PMID: 33987695 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
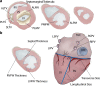
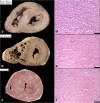
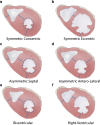
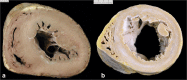
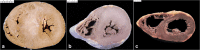
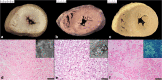
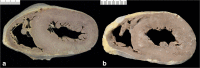
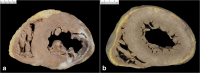
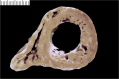
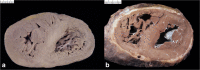
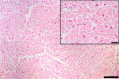
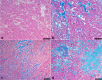
Since cardiac hypertrophy may be considered a cause of death at autopsy, its assessment requires a uniform approach. Common terminology and methodology to measure the heart weight, size, and thickness as well as a systematic use of cut off values for normality by age, gender, and body weight and height are needed. For these reasons, recommendations have been written on behalf of the Association for European Cardiovascular Pathology. The diagnostic work up implies the search for pressure and volume overload conditions, compensatory hypertrophy, storage and infiltrative disorders, and cardiomyopathies. Although some gross morphologic features can point to a specific diagnosis, systematic histologic analysis, followed by possible immunostaining and transmission electron microscopy, is essential for a final diagnosis. If the autopsy is carried out in a general or forensic pathology service without expertise in cardiovascular pathology, the entire heart (or pictures) together with mapped histologic slides should be sent for a second opinion to a pathologist with such an expertise. Indication for postmortem genetic testing should be integrated into the multidisciplinary management of sudden cardiac death.
Keywords: Autopsy; Cardiovascular diseases; Diagnostic criteria; Hypertrophy; Quality in pathology.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Basso C, Aguilera B, Banner J, Cohle S, d'Amati G, de Gouveia RH, di Gioia C, Fabre A, Gallagher PJ, Leone O, Lucena J, Mitrofanova L, Molina P, Parsons S, Rizzo S, Sheppard MN, Mier MPS, Suvarna SK, Thiene G, van der Wal A, Vink A, Michaud K, Association for European Cardiovascular Pathology Guidelines for autopsy investigation of sudden cardiac death: 2017 update from the Association for European Cardiovascular Pathology. Virchows Arch. 2017;471(6):691–705. doi: 10.1007/s00428-017-2221-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Elliott PM, Anastasakis A, Borger MA, Borggrefe M, Cecchi F, Charron P, Hagege AA, Lafont A, Limongelli G, Mahrholdt H, McKenna WJ, Mogensen J, Nihoyannopoulos P, Nistri S, Pieper PG, Pieske B, Rapezzi C, Rutten FH, Tillmanns C, Watkins H. ESC Guidelines on diagnosis and management of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur Heart J. 2014;35(39):2733–2779. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu284. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Maron BJ, Towbin JA, Thiene G, Antzelevitch C, Corrado D, Arnett D, Moss AJ, Seidman CE, Young JB, American Heart Association. Council on Clinical Cardiology, Heart Failure and Transplantation Committee. Quality of Care and Outcomes Research and Functional Genomics and Translational Biology Interdisciplinary Working Groups. Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Contemporary definitions and classification of the cardiomyopathies: an American Heart Association Scientific Statement from the Council on Clinical Cardiology, Heart Failure and Transplantation Committee; Quality of Care and Outcomes Research and Functional Genomics and Translational Biology Interdisciplinary Working Groups; and Council on Epidemiology and Prevention. Circulation. 2006;113(14):1807–1816. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.174287. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Elliott P, Andersson B, Arbustini E, Bilinska Z, Cecchi F, Charron P, Dubourg O, Kühl U, Maisch B, McKenna WJ, Monserrat L, Pankuweit S, Rapezzi C, Seferovic P, Tavazzi L, Keren A. Classification of the cardiomyopathies: a position statement from the European Society Of Cardiology Working Group on Myocardial and Pericardial Diseases. Eur Heart J. 2008;29(2):270–276. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehm342. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

