Preclinical Optimization and Safety Studies of a New Lentiviral Gene Therapy for p47phox-Deficient Chronic Granulomatous Disease
- PMID: 33740872
- PMCID: PMC8575060
- DOI: 10.1089/hum.2020.276
Preclinical Optimization and Safety Studies of a New Lentiviral Gene Therapy for p47phox-Deficient Chronic Granulomatous Disease
Abstract
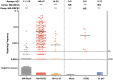
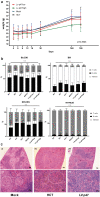
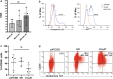
Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) is an inherited blood disorder of phagocytic cells that renders patients susceptible to infections and inflammation. A recent clinical trial of lentiviral gene therapy for the most frequent form of CGD, X-linked, has demonstrated stable correction over time, with no adverse events related to the gene therapy procedure. We have recently developed a parallel lentiviral vector for p47phox-deficient CGD (p47phoxCGD), the second most common form of this disease. Using this vector, we have observed biochemical correction of CGD in a mouse model of the disease. In preparation for clinical trial approval, we have performed standardized preclinical studies following Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) principles, to assess the safety of the gene therapy procedure. We report no evidence of adverse events, including mutagenesis and tumorigenesis, in human hematopoietic stem cells transduced with the lentiviral vector. Biodistribution studies of transduced human CD34+ cells indicate that the homing properties or engraftment ability of the stem cells is not negatively affected. CD34+ cells derived from a p47phoxCGD patient were subjected to an optimized transduction protocol and transplanted into immunocompromised mice. After the procedure, patient-derived neutrophils resumed their function, suggesting that gene correction was successful. These studies pave the way to a first-in-man clinical trial of lentiviral gene therapy for the treatment of p47phoxCGD.
Keywords: biodistribution; chronic granulomatous disease; genotoxicity; lentiviral gene therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. A.J.T. is on the Scientific Advisory Board of Orchard Therapeutics and Rocket Pharmaceuticals. H.L.M. is on the Scientific Advisory Board of Orchard Therapeutics and on the Safety Monitoring Board of Rocket Pharmaceuticals. H.B.G. is Chief Executive Officer for Orchard Therapeutics.
Figures

References
-
- Koker MY, Camcioglu Y, van Leeuwen K, et al. Clinical, functional, and genetic characterization of chronic granulomatous disease in 89 Turkish patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2013;132:1156–1163.e5. - PubMed
-
- Tajik S, Badalzadeh M, Fazlollahi MR, et al. Genetic and molecular findings of 38 Iranian patients with chronic granulomatous disease caused by p47-phox defect. Scand J Immunol 2019;90:e12767. - PubMed
-
- Kutukculer N, Aykut A, Karaca NE, et al. Chronic granulamatous disease: two decades of experience from a paediatric immunology unit in a country with high rate of consangineous marriages. Scand J Immunol 2019;89:e12737. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
