Research on the predictive effect of a combined model of ARIMA and neural networks on human brucellosis in Shanxi Province, China: a time series predictive analysis
- PMID: 33740904
- PMCID: PMC7980350
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-021-05973-4
Research on the predictive effect of a combined model of ARIMA and neural networks on human brucellosis in Shanxi Province, China: a time series predictive analysis
Abstract
Background: Brucellosis is a major public health problem that seriously affects developing countries and could cause significant economic losses to the livestock industry and great harm to human health. Reasonable prediction of the incidence is of great significance in controlling brucellosis and taking preventive measures.
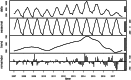
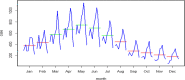
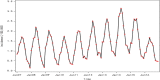
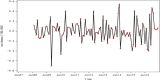
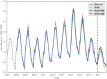
Methods: Our human brucellosis incidence data were extracted from Shanxi Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention. We used seasonal-trend decomposition using Loess (STL) and monthplot to analyse the seasonal characteristics of human brucellosis in Shanxi Province from 2007 to 2017. The autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) model, a combined model of ARIMA and the back propagation neural network (ARIMA-BPNN), and a combined model of ARIMA and the Elman recurrent neural network (ARIMA-ERNN) were established separately to make predictions and identify the best model. Additionally, the mean squared error (MAE), mean absolute error (MSE) and mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) were used to evaluate the performance of the model.
Results: We observed that the time series of human brucellosis in Shanxi Province increased from 2007 to 2014 but decreased from 2015 to 2017. It had obvious seasonal characteristics, with the peak lasting from March to July every year. The best fitting and prediction effect was the ARIMA-ERNN model. Compared with those of the ARIMA model, the MAE, MSE and MAPE of the ARIMA-ERNN model decreased by 18.65, 31.48 and 64.35%, respectively, in fitting performance; in terms of prediction performance, the MAE, MSE and MAPE decreased by 60.19, 75.30 and 64.35%, respectively. Second, compared with those of ARIMA-BPNN, the MAE, MSE and MAPE of ARIMA-ERNN decreased by 9.60, 15.73 and 11.58%, respectively, in fitting performance; in terms of prediction performance, the MAE, MSE and MAPE decreased by 31.63, 45.79 and 29.59%, respectively.
Conclusions: The time series of human brucellosis in Shanxi Province from 2007 to 2017 showed obvious seasonal characteristics. The fitting and prediction performances of the ARIMA-ERNN model were better than those of the ARIMA-BPNN and ARIMA models. This will provide some theoretical support for the prediction of infectious diseases and will be beneficial to public health decision making.
Keywords: ARIMA-BPNN model; ARIMA-ERNN model; Human brucellosis; Predictive effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no comprting interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Study on the prediction effect of a combined model of SARIMA and LSTM based on SSA for influenza in Shanxi Province, China.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Feb 6;23(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08025-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 36747126 Free PMC article.
-
ARIMA and ARIMA-ERNN models for prediction of pertussis incidence in mainland China from 2004 to 2021.BMC Public Health. 2022 Jul 29;22(1):1447. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-13872-9. BMC Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35906580 Free PMC article.
-
Time series analysis of human brucellosis in mainland China by using Elman and Jordan recurrent neural networks.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 May 14;19(1):414. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4028-x. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31088391 Free PMC article.
-
Autoregressive models in environmental forecasting time series: a theoretical and application review.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023 Feb;30(8):19617-19641. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-25148-9. Epub 2023 Jan 17. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36648728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transmission dynamics of brucellosis: Mathematical modelling and applications in China.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020 Nov 21;18:3843-3860. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.11.014. eCollection 2020. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020. PMID: 33335683 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spatial-temporal analysis of hepatitis E in Hainan Province, China (2013-2022): insights from four major hospitals.Front Public Health. 2024 Jun 27;12:1381204. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1381204. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38993698 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the prediction effect of a combined model of SARIMA and LSTM based on SSA for influenza in Shanxi Province, China.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Feb 6;23(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08025-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 36747126 Free PMC article.
-
The research on TBATS and ELM models for prediction of human brucellosis cases in mainland China: a time series study.BMC Infect Dis. 2022 Dec 12;22(1):934. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07919-w. BMC Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 36510150 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology and time series analysis of human brucellosis in Tebessa province, Algeria, from 2000 to 2020.J Res Health Sci. 2022 Mar 2;22(1):e00544. doi: 10.34172/jrhs.2022.79. J Res Health Sci. 2022. PMID: 36511254 Free PMC article.
-
The research of ARIMA, GM(1,1), and LSTM models for prediction of TB cases in China.PLoS One. 2022 Feb 23;17(2):e0262734. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0262734. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35196309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaan JA, Frakking FNJ, Arents NLA, Anten S, Roest HIJ, Rothbarth PH. Clinical manifestations and hazards of brucellosis in the Netherlands. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2012;156(12):A4460. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

