Wilms' tumor gene 1 is an independent prognostic factor for pediatric acute myeloid leukemia following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- PMID: 33740924
- PMCID: PMC7980537
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-08022-0
Wilms' tumor gene 1 is an independent prognostic factor for pediatric acute myeloid leukemia following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Abstract
Background: Sequential monitoring of Wilms' tumor gene 1 (WT1) after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) could predict relapse in adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML). However, the prognostic role of WT1 in pediatric AML after allo-HSCT is unclear. Thus, we determined to see whether sequential monitoring of WT1 after allo-HSCT could predict relapse in AML children.
Methods: Pediatric AML patients receiving allo-HSCT from January 21, 2012 to December 20, 2018 at the Peking University Institute of Hematology were included in this study. WT1 expression level was determined by TaqMan-based reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. WT1 sequential monitoring was performed 1, 2, 3, 4.5, 6, 9, and 12 months post-transplantation and at 6-month intervals thereafter. The primary end point was relapse. The secondary end points included disease-free survival (DFS), overall survival (OS), and non-relapse mortality (NRM). Kaplan-Meier analysis was used for DFS and OS estimates, while competing risk analysis was used for estimating relapse and NRM.
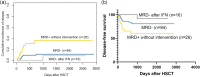
Results: Of the 151 consecutive patients included, the median age was 10 years (range, 1-17). The optimal cutoff value of WT1 within 1 year after allo-HSCT to predict relapse was 0.8% (80 WT1 copies/104 ABL copies), with a sensitivity of 60% and specificity of 79%. Compared with WT1 expression < 0.8%, WT1 expression ≥0.8% indicated significantly higher 5-year cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR, 35.1% vs. 11.3%; P = 0.001), lower 5-year disease-free survival (DFS, 60.4% vs. 80.8%; P = 0.009), and lower 5-year overall survival (OS, 64.9% vs. 81.6%; P = 0.038) rates. Multivariate analyses showed that WT1 was an independent risk factor for relapse (HR 2.89; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.25-6.71; P = 0.014). Both the CIR (5-year CIR: 8.3% vs. 11.3%; P = 0.513) and DFS (5-year DFS: 91.7% vs. 80.8%; P = 0.208) were comparable between patients achieving minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity after preemptive interferon-α (IFN-α) treatment and those without MRD after allo-HSCT, which were better than those of MRD-positive patients without preemptive therapies.
Conclusions: Sequential monitoring of WT1 could predict relapse in pediatric AML after allo-HSCT. WT1-directed immunotherapy may have the potential to prevent relapse and improve survival.
Keywords: Acute myeloid leukemia; Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; Pediatric; Relapse; Wilms’ tumor gene 1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Efficacy of WT1 gene-guided pre-emptive therapy for prevention of relapse in acute myeloid leukemia after transplantation and its optimal intervention threshold.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Jul 28;49(7):1120-1129. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.240351. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 39788500 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
High prognostic value of pre-allogeneic stem cell transplantation minimal residual disease detection by WT1 gene expression in AML transplanted in cytologic complete remission.Leuk Res. 2017 Dec;63:22-27. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2017.10.010. Epub 2017 Oct 27. Leuk Res. 2017. PMID: 29096332
-
WT1 Gene Expression in Peripheral Blood Before and After Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation is a Clinically Relevant Prognostic Marker in AML - A Single-center 14-year Experience.Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2021 Feb;21(2):e145-e151. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2020.09.008. Epub 2020 Oct 12. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2021. PMID: 33160932
-
Impact of BCOR/BCORL1 mutation on outcomes of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia patients.Ann Hematol. 2025 May;104(5):2631-2642. doi: 10.1007/s00277-025-06346-6. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Ann Hematol. 2025. PMID: 40202539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Outcomes with Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Therapy Related Myeloid Neoplasms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2025 May;25(5):e319-e335. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2024.12.018. Epub 2025 Jan 7. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2025. PMID: 39890517
Cited by
-
Efficacy of WT1 gene-guided pre-emptive therapy for prevention of relapse in acute myeloid leukemia after transplantation and its optimal intervention threshold.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Jul 28;49(7):1120-1129. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.240351. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 39788500 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
[Chinese expert consensus of the allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for pediatric acute myeloid leukemia (not APL) (2022)].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2022 Oct 14;43(10):802-809. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2022.10.002. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36709193 Free PMC article. Chinese. No abstract available.
-
Analysis of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Gene Expression Highlights the Role of Extracellular Vesicles in the Immune Response following Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Children.Genes (Basel). 2021 Dec 17;12(12):2008. doi: 10.3390/genes12122008. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34946957 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in immunotherapeutic targets for childhood cancers: A focus on glypican-2 and B7-H3.Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Jul;223:107892. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107892. Epub 2021 May 14. Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33992682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integration of measurable residual disease by WT1 gene expression and flow cytometry identifies pediatric patients with high risk of relapse in acute myeloid leukemia.Front Oncol. 2024 Apr 24;14:1340909. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1340909. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38720804 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu L, Chen H, Chen J, Han M, Huang H, Lai Y, Liu D, Liu Q, Liu T, Jiang M, Ren H, Song Y, Sun Z, Wang J, Wu D, Zhou D, Zou P, Liu K, Huang X. The consensus on indications, conditioning regimen, and donor selection of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for hematological diseases in China-recommendations from the Chinese Society of Hematology. J Hematol Oncol. 2018;11(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13045-018-0564-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

