RNA-based therapies: A cog in the wheel of lung cancer defense
- PMID: 33740988
- PMCID: PMC7977189
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-021-01338-2
RNA-based therapies: A cog in the wheel of lung cancer defense
Abstract
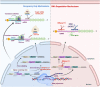
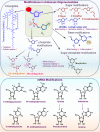
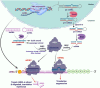
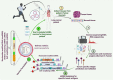
Lung cancer (LC) is a heterogeneous disease consisting mainly of two subtypes, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC), and remains the leading cause of death worldwide. Despite recent advances in therapies, the overall 5-year survival rate of LC remains less than 20%. The efficacy of current therapeutic approaches is compromised by inherent or acquired drug-resistance and severe off-target effects. Therefore, the identification and development of innovative and effective therapeutic approaches are critically desired for LC. The development of RNA-mediated gene inhibition technologies was a turning point in the field of RNA biology. The critical regulatory role of different RNAs in multiple cancer pathways makes them a rich source of targets and innovative tools for developing anticancer therapies. The identification of antisense sequences, short interfering RNAs (siRNAs), microRNAs (miRNAs or miRs), anti-miRs, and mRNA-based platforms holds great promise in preclinical and early clinical evaluation against LC. In the last decade, RNA-based therapies have substantially expanded and tested in clinical trials for multiple malignancies, including LC. This article describes the current understanding of various aspects of RNA-based therapeutics, including modern platforms, modifications, and combinations with chemo-/immunotherapies that have translational potential for LC therapies.
Keywords: Antisense oligonucleotides; Lung cancer; RNA interference; anti-miRs; mRNA-vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
SKB is co-founder of Sanguine Diagnostics and Therapeutics, Inc. AKG is on the advisory board for Blueprint Medicines, Cardinal Health, AstraZeneca, and G1 Therapeutics. He has served as a consultant to AstraZeneca and Genentech, and received research support from Oncoceutics and Takeda Pharmaceuticals. Other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

