Exosomal miR-106b-5p derived from melanoma cell promotes primary melanocytes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through targeting EphA4
- PMID: 33741023
- PMCID: PMC7980627
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-021-01906-w
Exosomal miR-106b-5p derived from melanoma cell promotes primary melanocytes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through targeting EphA4
Abstract
Background: Cancer-secreted exosomal miRNAs regulates the biological processes of many tumours. The serum level of exosomal miR-106b-5p is significantly increased in melanoma patients. However, the role and molecular mechanisms of exosomal miR-106b-5p in melanoma remains unclear.
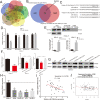
Methods: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was used to detect the expression of miR-106b-5p and EphA4 in melanoma tissues. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and western blotting were used to identify exosome. QRT-qPCR and Cy3-labelled miR-106b-5p were used to demonstrated the transmission of melanoma cell-secreted exosomal miR-106b-5p. Western blotting, Immunofluorescence, adhesion, transwell and scratch wound assay were used to explore the role of exosomal miR-106b-5p in melanocytes. Luciferase reporter assays and RNA-Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay were used to confirm whether erythropoietin-producing hepatocellular carcinoma receptor A4 (EphA4) was a direct target of miR-106b-5p.
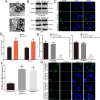
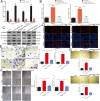
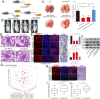
Results: We found that miR-106b-5p levels were increased in melanoma tissue, and high miR-106b-5p expression is an independent risk factor for the overall survival of patients with melanoma. miR-106b-5p is enriched in melanoma cell-secreted exosomes and transferred to melanocytes. Exosomal miR-106b-5p promotes the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), migration, invasion and adhesion of melanocytes. Exosomal miR-106b-5p exerted its role by targeting EphA4 to activate the ERK pathway. We demonstrated that exosomal miR-106b-5p promoted melanoma metastasis in vivo through pulmonary metastasis assay.
Conclusions: Thus, melanoma cell-secreted exosomal miR-106b-5p may serve as a diagnostic indicator and potential therapeutic target in melanoma patients.
Keywords: EMT; EphA4; Exosomal; Melanoma; miR-106b-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

