JAK selectivity and the implications for clinical inhibition of pharmacodynamic cytokine signalling by filgotinib, upadacitinib, tofacitinib and baricitinib
- PMID: 33741556
- PMCID: PMC8237188
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-219012
JAK selectivity and the implications for clinical inhibition of pharmacodynamic cytokine signalling by filgotinib, upadacitinib, tofacitinib and baricitinib
Abstract
Objective: Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKinibs) are efficacious in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) with variable reported rates of adverse events, potentially related to differential JAK family member selectivity. Filgotinib was compared with baricitinib, tofacitinib and upadacitinib to elucidate the pharmacological basis underlying its clinical efficacy and safety.
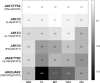
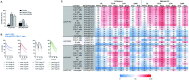
Methods: In vitro JAKinib inhibition of signal transducer and activator of transcription phosphorylation (pSTAT) was measured by flow cytometry in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and whole blood from healthy donors and patients with RA following cytokine stimulation of distinct JAK/STAT pathways. The average daily pSTAT and time above 50% inhibition were calculated at clinical plasma drug exposures in immune cells. The translation of these measures was evaluated in ex vivo-stimulated assays in phase 1 healthy volunteers.
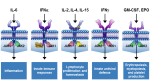
Results: JAKinib potencies depended on cytokine stimulus, pSTAT readout and cell type. JAK1-dependent pathways (interferon (IFN)α/pSTAT5, interleukin (IL)-6/pSTAT1) were among the most potently inhibited by all JAKinibs in healthy and RA blood, with filgotinib exhibiting the greatest selectivity for JAK1 pathways. Filgotinib (200 mg once daily) had calculated average daily target inhibition for IFNα/pSTAT5 and IL-6/pSTAT1 that was equivalent to tofacitinib (5 mg two times per day), upadacitinib (15 mg once daily) and baricitinib (4 mg once daily), with the least average daily inhibition for the JAK2-dependent and JAK3-dependent pathways including IL-2, IL-15, IL-4 (JAK1/JAK3), IFNγ (JAK1/JAK2), granulocyte colony stimulating factor, IL-12, IL-23 (JAK2/tyrosine kinase 2) and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (JAK2/JAK2). Ex vivo pharmacodynamic data from phase 1 healthy volunteers clinically confirmed JAK1 selectivity of filgotinib.
Conclusion: Filgotinib inhibited JAK1-mediated signalling similarly to other JAKinibs, but with less inhibition of JAK2-dependent and JAK3-dependent pathways, providing a mechanistic rationale for its apparently differentiated efficacy:safety profile.
Keywords: antirheumatic agents; arthritis; cytokines; immune system diseases; rheumatoid.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: PGT, BM, FC, AM and JAD are employees of Gilead Sciences, Inc. RG is an employee of Galapagos SASU.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

