Cytochromes in Extracellular Electron Transfer in Geobacter
- PMID: 33741623
- PMCID: PMC8117768
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.03109-20
Cytochromes in Extracellular Electron Transfer in Geobacter
Abstract
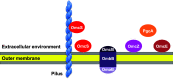
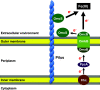
Extracellular electron transfer (EET) is an important biological process in microbial physiology as found in dissimilatory metal oxidation/reduction and interspecies electron transfer in syntrophy in natural environments. EET also plays a critical role in microorganisms relevant to environmental biotechnology in metal-contaminated areas, metal corrosion, bioelectrochemical systems, and anaerobic digesters. Geobacter species exist in a diversity of natural and artificial environments. One of the outstanding features of Geobacter species is the capability of direct EET with solid electron donors and acceptors, including metals, electrodes, and other cells. Therefore, Geobacter species are pivotal in environmental biogeochemical cycles and biotechnology applications. Geobacter sulfurreducens, a representative Geobacter species, has been studied for direct EET as a model microorganism. G. sulfurreducens employs electrically conductive pili (e-pili) and c-type cytochromes for the direct EET. The biological function and electronics applications of the e-pili have been reviewed recently, and this review focuses on the cytochromes. Geobacter species have an unusually large number of cytochromes encoded in their genomes. Unlike most other microorganisms, Geobacter species localize multiple cytochromes in each subcellular fraction, outer membrane, periplasm, and inner membrane, as well as in the extracellular space, and differentially utilize these cytochromes for EET with various electron donors and acceptors. Some of the cytochromes are functionally redundant. Thus, the EET in Geobacter is complicated. Geobacter coordinates the cytochromes with other cellular components in the elaborate EET system to flourish in the environment.
Keywords: Geobacter; cytochrome; extracellular electron transfer.
Copyright © 2021 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

References
-
- Koch C, Harnisch F. 2016. Is there a specific ecological niche for electroactive microorganisms? ChemElectroChem 3:1282–1295. 10.1002/celc.201600079. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

