CRISPRi screens reveal a DNA methylation-mediated 3D genome dependent causal mechanism in prostate cancer
- PMID: 33741908
- PMCID: PMC7979745
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-21867-0
CRISPRi screens reveal a DNA methylation-mediated 3D genome dependent causal mechanism in prostate cancer
Abstract
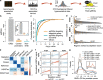
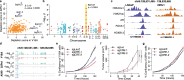
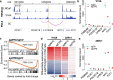
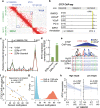
Prostate cancer (PCa) risk-associated SNPs are enriched in noncoding cis-regulatory elements (rCREs), yet their modi operandi and clinical impact remain elusive. Here, we perform CRISPRi screens of 260 rCREs in PCa cell lines. We find that rCREs harboring high risk SNPs are more essential for cell proliferation and H3K27ac occupancy is a strong indicator of essentiality. We also show that cell-line-specific essential rCREs are enriched in the 8q24.21 region, with the rs11986220-containing rCRE regulating MYC and PVT1 expression, cell proliferation and tumorigenesis in a cell-line-specific manner, depending on DNA methylation-orchestrated occupancy of a CTCF binding site in between this rCRE and the MYC promoter. We demonstrate that CTCF deposition at this site as measured by DNA methylation level is highly variable in prostate specimens, and observe the MYC eQTL in the 8q24.21 locus in individuals with low CTCF binding. Together our findings highlight a causal mechanism synergistically driven by a risk SNP and DNA methylation-mediated 3D genome architecture, advocating for the integration of genetics and epigenetics in assessing risks conferred by genetic predispositions.
Conflict of interest statement
Felix Y. Feng is co-founder of PFS Genomics and serves on the Scientific Advisory Board of SerImmune.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

