Development of a rapid scabies immunodiagnostic assay based on transcriptomic analysis of Sarcoptes scabiei var. nyctereutis
- PMID: 33742008
- PMCID: PMC7979781
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-85290-7
Development of a rapid scabies immunodiagnostic assay based on transcriptomic analysis of Sarcoptes scabiei var. nyctereutis
Abstract
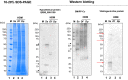
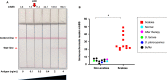
Scabies is a highly contagious skin disease caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei that affects many mammals. However, the sensitivity of traditional tests for scabies diagnosis in humans is less than 50%. To simplify the diagnosis of scabies, methods that are simple, sensitive, specific, and cost-effective are required. We developed an immunodiagnostic test based on S. scabiei var. nyctereutis RNA-seq data collected from Japanese raccoon dogs with sarcoptic mange. Three candidate antigens-a highly expressed hypothetical protein "QR98_0091190," another mite allergen known as "SMIPP-Cc," and an abundant "vitellogenin-like protein"-were evaluated by western-blot analysis. A lateral flow immunoassay, using specific antibodies against the vitellogenin-like protein, successfully detected scabies in the skin flakes of S. scabiei-infected raccoon dogs. This assay can potentially diagnose scabies more accurately in wildlife, as well as in humans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The complete mitochondrial genome of Sarcoptes scabiei var. nyctereutis from the Japanese raccoon dog: Prediction and detection of two transfer RNAs (tRNA-A and tRNA-Y).Genomics. 2019 Dec;111(6):1183-1191. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2018.09.002. Epub 2018 Sep 15. Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30223010
-
Vaccination of rabbits with immunodominant antigens from Sarcoptes scabiei induced high levels of humoral responses and pro-inflammatory cytokines but confers limited protection.Parasit Vectors. 2016 Aug 8;9(1):435. doi: 10.1186/s13071-016-1717-9. Parasit Vectors. 2016. PMID: 27502394 Free PMC article.
-
New techniques to collect live Sarcoptes scabiei and evaluation of methods as alternative diagnostics for infection.Parasitol Res. 2017 Mar;116(3):1039-1042. doi: 10.1007/s00436-017-5385-2. Epub 2017 Jan 26. Parasitol Res. 2017. PMID: 28124136
-
Problems in diagnosing scabies, a global disease in human and animal populations.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2007 Apr;20(2):268-79. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00042-06. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2007. PMID: 17428886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host immune responses to the itch mite, Sarcoptes scabiei, in humans.Parasit Vectors. 2017 Aug 10;10(1):385. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2320-4. Parasit Vectors. 2017. PMID: 28797273 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic analysis of Sarcoptes scabiei reveals that proteins differentially expressed between eggs and female adult stages are involved predominantly in genetic information processing, metabolism and/or host-parasite interactions.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022 Dec 6;16(12):e0010946. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010946. eCollection 2022 Dec. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022. PMID: 36472966 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting host range expansion in parasitic mites using a global mammalian-acarine dataset.Nat Commun. 2024 Jun 26;15(1):5431. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49515-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38926409 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bornstein S, Mörner T, Samuel WM. Sarcoptes scabiei and sarcoptic mange. In: Samuel WM, Pybus MJ, Kocan AA, editors. Parasitic Disease of Wild Mammals. 2. Iowa: Iowa State University Press; 2001. pp. 107–119.
-
- Engelman D, Yoshizumi J, Hay RJ, Osti M, Micali G, Norton S, Walton S, Boralevi F, Bernigaud C, Bowen AC, Chang AY, Chosidow O, Estrada-Chavez G, Feldmeier H, Ishii N, Lacarrubba F, Mahé A, Maurer T, Mahdi MMA, Murdoch ME, Pariser D, Nair PA, Rehmus W, Romani L, Tilakaratne D, Tuicakau M, Walker SL, Wanat KA, Whitfeld MJ, Yotsu RR, Steer AC, Fuller LC. The 2020 international alliance for the control of scabies consensus criteria for the diagnosis of scabies. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020;183(5):808–820. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18943. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

