HDL biodistribution and brain receptors in zebrafish, using HDLs as vectors for targeting endothelial cells and neural progenitors
- PMID: 33742021
- PMCID: PMC7979862
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-85183-9
HDL biodistribution and brain receptors in zebrafish, using HDLs as vectors for targeting endothelial cells and neural progenitors
Abstract
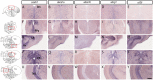
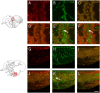
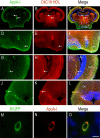
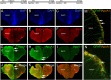
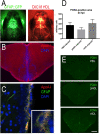
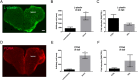
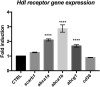
High density lipoproteins (HDLs) display pleiotropic functions such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-protease, and anti-apoptotic properties. These effects are mediated by four main receptors: SCARB1 (SR-BI), ABCA1, ABCG1, and CD36. Recently, HDLs have emerged for their potential involvement in brain functions, considering their epidemiological links with cognition, depression, and brain plasticity. However, their role in the brain is not well understood. Given that the zebrafish is a well-recognized model for studying brain plasticity, metabolic disorders, and apolipoproteins, it could represent a good model for investigating the role of HDLs in brain homeostasis. By analyzing RNA sequencing data sets and performing in situ hybridization, we demonstrated the wide expression of scarb1, abca1a, abca1b, abcg1, and cd36 in the brain of adult zebrafish. Scarb1 gene expression was detected in neural stem cells (NSCs), suggesting a possible role of HDLs in NSC activity. Accordingly, intracerebroventricular injection of HDLs leads to their uptake by NSCs without modulating their proliferation. Next, we studied the biodistribution of HDLs in the zebrafish body. In homeostatic conditions, intraperitoneal injection of HDLs led to their accumulation in the liver, kidneys, and cerebral endothelial cells in zebrafish, similar to that observed in mice. After telencephalic injury, HDLs were diffused within the damaged parenchyma and were taken up by ventricular cells, including NSCs. However, they failed to modulate the recruitment of microglia cells at the injury site and the injury-induced proliferation of NSCs. In conclusion, our results clearly show a functional HDL uptake process involving several receptors that may impact brain homeostasis and suggest the use of HDLs as delivery vectors to target NSCs for drug delivery to boost their neurogenic activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
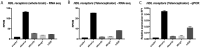

Similar articles
-
Gene expression patterns of the LDL receptor and its inhibitor Pcsk9 in the adult zebrafish brain suggest a possible role in neurogenesis.Eur J Neurosci. 2025 Jan;61(1):e16586. doi: 10.1111/ejn.16586. Epub 2024 Nov 17. Eur J Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39551948 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the cellular expression patterns of vascular endothelial growth factor aa and bb genes and their receptors in the adult zebrafish brain during constitutive and regenerative neurogenesis.Neural Dev. 2024 Sep 12;19(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13064-024-00195-1. Neural Dev. 2024. PMID: 39267104 Free PMC article.
-
HDL and endothelial protection.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Jun;169(3):493-511. doi: 10.1111/bph.12174. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23488589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uptake and transport of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and HDL-associated alpha-tocopherol by an in vitro blood-brain barrier model.J Neurochem. 2004 May;89(4):939-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02373.x. J Neurochem. 2004. PMID: 15140193
-
High-density lipoproteins and immune response: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2022 Jan 15;195:117-123. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.12.009. Epub 2021 Dec 9. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022. PMID: 34896462 Review.
Cited by
-
Gene expression patterns of the LDL receptor and its inhibitor Pcsk9 in the adult zebrafish brain suggest a possible role in neurogenesis.Eur J Neurosci. 2025 Jan;61(1):e16586. doi: 10.1111/ejn.16586. Epub 2024 Nov 17. Eur J Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39551948 Free PMC article.
-
Telencephalic stab wound injury induces regenerative angiogenesis and neurogenesis in zebrafish: unveiling the role of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling and microglia.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Oct 1;20(10):2938-2954. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-01881. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 39248179 Free PMC article.
-
Roles and Therapeutic Implications of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jul 22;10(8):1167. doi: 10.3390/antiox10081167. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ApoA-I Nanoparticles as Curcumin Carriers for Cerebral Endothelial Cells: Improved Cytoprotective Effects against Methylglyoxal.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Mar 13;15(3):347. doi: 10.3390/ph15030347. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35337146 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the cellular expression patterns of vascular endothelial growth factor aa and bb genes and their receptors in the adult zebrafish brain during constitutive and regenerative neurogenesis.Neural Dev. 2024 Sep 12;19(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13064-024-00195-1. Neural Dev. 2024. PMID: 39267104 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

