The factors influencing clinical outcomes after leukapheresis in acute leukaemia
- PMID: 33742034
- PMCID: PMC7979875
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-85918-8
The factors influencing clinical outcomes after leukapheresis in acute leukaemia
Abstract
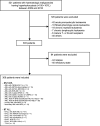
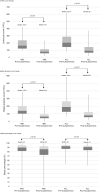
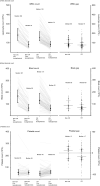
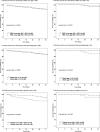
Leukapheresis is used for the mechanical removal of leukaemic cells in hyperleukocytosis. However, the effectiveness of leukapheresis remains unclear due to selection and confounding factors in the cohorts. We compared the effectiveness of leukapheresis among the subgroups according to either the 2016 World Health Organization classification or the number of cytogenetic abnormalities with a retrospective, single-centre study from January 2009 to December 2018. Acute myeloid leukaemia (AML, n = 212) and acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL, n = 97) were included. The 30-day survival rates (95% confidence interval, 95% CI) for AML and ALL were 86.3% (81.6-90.9%) and 94.8% (90.3-99.2%), respectively. For AML, 'primary AML with myelodysplasia-related changes' and 'AML with biallelic mutation of CEBPA' showed better 30-day survival outcomes (P = 0.026) than the other subgroups. A higher platelet count after leukapheresis was associated with better 30-day survival in AML patients (P = 0.029). A decrease in blast percentage count after leukapheresis was associated with better 30-day survival in ALL patients (P = 0.034). Our study suggested that prophylactic platelet transfusion to raise the platelet count to 50 × 109/L or greater might improve clinical outcome in AML patients undergoing leukapheresis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Leukapheresis and exchange transfusion in children with acute leukemia and hyperleukocytosis. A single center experience.Klin Padiatr. 2009 Nov-Dec;221(6):374-8. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1239533. Epub 2009 Nov 4. Klin Padiatr. 2009. PMID: 19890790
-
Early Complications of Hyperleukocytosis and Leukapheresis in Childhood Acute Leukemias.J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2016 Mar;38(2):111-7. doi: 10.1097/MPH.0000000000000490. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26794706
-
Leukapheresis in acute myeloid leukemia patients with hyperleukocytosis: A single center experience.Transfus Apher Sci. 2015 Oct;53(2):185-90. doi: 10.1016/j.transci.2015.03.015. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Transfus Apher Sci. 2015. PMID: 25843763
-
Hyperleukocytosis and leukocytapheresis in acute leukaemias: experience from a single centre and review of the literature of leukocytapheresis in acute myeloid leukaemia.Transfus Med. 2013 Dec;23(6):397-406. doi: 10.1111/tme.12067. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Transfus Med. 2013. PMID: 23919332 Review.
-
CCAAT enhancer binding protein alpha (CEBPA) biallelic acute myeloid leukaemia: cooperating lesions, molecular mechanisms and clinical relevance.Br J Haematol. 2020 Aug;190(4):495-507. doi: 10.1111/bjh.16534. Epub 2020 Feb 21. Br J Haematol. 2020. PMID: 32086816 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Machine Learning Predicts 30-Day Outcome among Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients: A Single-Center, Retrospective, Cohort Study.J Clin Med. 2023 Sep 13;12(18):5940. doi: 10.3390/jcm12185940. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37762881 Free PMC article.
-
Risk stratification by 30-day prognostic factors of clinical outcomes after granulocyte transfusion in acute myeloid leukemia: A single-center retrospective study.PLoS One. 2022 Aug 30;17(8):e0273827. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273827. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36040987 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics and outcomes of children with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia and hyperleukocytosis managed with different cytoreductive methods.Cancer. 2023 Jun 15;129(12):1873-1884. doi: 10.1002/cncr.34751. Epub 2023 Mar 21. Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36943896 Free PMC article.
-
T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Crisis: Hyperleukocytosis, Tumor Lysis Syndrome, and Innovative Approaches.Cureus. 2024 Jan 10;16(1):e52017. doi: 10.7759/cureus.52017. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38344604 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

