A single donor is sufficient to produce a highly functional in vitro antibody library
- PMID: 33742103
- PMCID: PMC7979914
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-021-01881-0
A single donor is sufficient to produce a highly functional in vitro antibody library
Abstract
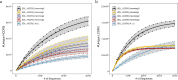
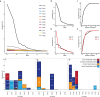
Antibody complementarity determining region diversity has been considered to be the most important metric for the production of a functional antibody library. Generally, the greater the antibody library diversity, the greater the probability of selecting a diverse array of high affinity leads. According to this paradigm, the primary means of elevating library diversity has been by increasing the number of donors. In the present study we explored the possibility of creating an in vitro antibody library from a single healthy individual, showing that the number of lymphocytes, rather than the number of donors, is the key criterion in the production of a diverse and functional antibody library. We describe the construction of a high-quality phage display library comprising 5 × 109 human antibodies by applying an efficient B cell extraction protocol from a single donor and a targeted V-gene amplification strategy favoring specific antibody families for their improved developability profiles. Each step of the library generation process was followed and validated by next generation sequencing to monitor the library quality and diversity. The functionality of the library was tested using several therapeutically relevant targets for which a vast number of different antibodies with desired biophysical properties were obtained.
Conflict of interest statement
M. Frank Erasmus, Sara D’Angelo, Fortunato Ferrara, Leslie Naranjo, and Andrew R.M. Bradbury are employees and stockholders of Specifica Inc. Rebecca Buonpane, Shaun M. Stewart, and Horacio G. Nastri are employees and stockholders of Incyte Corp. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Drug-like antibodies with high affinity, diversity and developability directly from next-generation antibody libraries.MAbs. 2021 Jan-Dec;13(1):1980942. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2021.1980942. MAbs. 2021. PMID: 34850665 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing CDRH3 diversity captured from secondary lymphoid organs for the generation of recombinant human antibodies.MAbs. 2013 Sep-Oct;5(5):690-8. doi: 10.4161/mabs.25592. Epub 2013 Jul 2. MAbs. 2013. PMID: 23924800 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Synthetic Antibody Library with Complementarity-Determining Region Diversities Designed for an Improved Amplification Profile.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 2;23(11):6255. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116255. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682935 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic antibodies: concepts, potential and practical considerations.Methods. 2012 Aug;57(4):486-98. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.06.012. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Methods. 2012. PMID: 22750306 Review.
-
Therapeutic Antibodies by Phage Display.Curr Pharm Des. 2016;22(43):6538-6559. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666160923113714. Curr Pharm Des. 2016. PMID: 27669967 Review.
Cited by
-
Mammalian display to secretion switchable libraries for antibody preselection and high throughput functional screening.MAbs. 2023 Jan-Dec;15(1):2251190. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2023.2251190. MAbs. 2023. PMID: 37646089 Free PMC article.
-
A next-generation Fab library platform directly yielding drug-like antibodies with high affinity, diversity, and developability.MAbs. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2394230. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2024.2394230. Epub 2024 Aug 27. MAbs. 2024. PMID: 39192463 Free PMC article.
-
Production Technologies for Recombinant Antibodies: Insights into Eukaryotic, Prokaryotic, and Transgenic Expression Systems.Biochem Genet. 2024 Sep 17. doi: 10.1007/s10528-024-10911-5. Online ahead of print. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 39287779
-
Progress and challenges for the machine learning-based design of fit-for-purpose monoclonal antibodies.MAbs. 2022 Jan-Dec;14(1):2008790. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2021.2008790. MAbs. 2022. PMID: 35293269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug-like antibodies with high affinity, diversity and developability directly from next-generation antibody libraries.MAbs. 2021 Jan-Dec;13(1):1980942. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2021.1980942. MAbs. 2021. PMID: 34850665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marks JD, et al. By-passing immunization. Human antibodies from V-gene libraries displayed on phage. J. Mol. Biol. 1991;222:581–597. - PubMed
-
- Vaughan TJ, et al. Human antibodies with sub-nanomolar affinities isolated from a large non-immunized phage display library. Nat. Biotechnol. 1996;14:309–314. - PubMed
-
- Sblattero D, Bradbury A. Exploiting recombination in single bacteria to make large phage antibody libraries. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000;18:75–80. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

