AHR in the intestinal microenvironment: safeguarding barrier function
- PMID: 33742166
- PMCID: PMC7611426
- DOI: 10.1038/s41575-021-00430-8
AHR in the intestinal microenvironment: safeguarding barrier function
Abstract
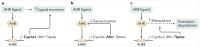
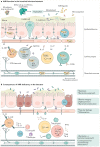
Mammalian aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) is a ligand-dependent transcription factor that belongs to the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)-PAS family of transcription factors, which are evolutionarily conserved environmental sensors. In the absence of ligands, AHR resides in the cytoplasm in a complex with molecular chaperones such as HSP90, XAP2 and p23. Upon ligand binding, AHR translocates into the nuclear compartment, where it dimerizes with its partner protein, AHR nuclear translocator (ARNT), an obligatory partner for the DNA-binding and functional activity. Historically, AHR had mostly been considered as a key intermediary for the detrimental effects of environmental pollutants on the body. However, following the discovery of AHR-mediated functions in various immune cells, as well as the emergence of non-toxic 'natural' AHR ligands, this view slowly began to change, and the study of AHR-deficient mice revealed a plethora of important beneficial functions linked to AHR activation. This Review focuses on regulation of the AHR pathway and the barrier-protective roles AHR has in haematopoietic, as well as non-haematopoietic, cells within the intestinal microenvironment. It covers the nature of AHR ligands and feedback regulation of the AHR pathway, outlining the currently known physiological functions in immune, epithelial, endothelial and neuronal cells of the intestine.
© 2021. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Schmidt JV, Bradfield CA. Ah receptor signaling pathways. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1996;12:55–89. - PubMed
-
- Veldhoen M, et al. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor links TH17-cell-mediated autoimmunity to environmental toxins. Nature. 2008;453:106–109. - PubMed
-
- Quintana FJ, et al. Control of Treg and TH17 cell differentiation by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Nature. 2008;453:65–71. - PubMed
-
- Stockinger B, Di Meglio P, Gialitakis M, Duarte JH. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: multitasking in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 2014;32:403–432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

