Associations between coronary heart disease and risk of cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 33742562
- PMCID: PMC8119850
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.2108
Associations between coronary heart disease and risk of cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Several studies have demonstrated that coronary heart disease (CHD) is a high risk factor for cognitive impairment, whereas other studies showed that there was no association between cognitive impairment and CHD. The relationship between CHD and cognitive impairment is still unclear based on these conflicting results. Thus, it is of importance to evaluate the association between CHD and cognitive impairment. The present study made a meta-analysis to explore the association between CHD and risk of cognitive impairment.
Methods: Articles exploring the association between CHD and cognitive impairment and published before November 2020 were searched in the following databases: PubMed, Web of Science, Medline, EMBASE, and Google Scholar. We used STATA 12.0 software to compute the relative risks (RRs), odds ratios (ORs), or hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
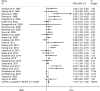
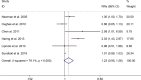
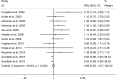
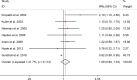
Results: The meta-analysis showed a positive association between CHD and risk of all-cause cognitive impairment with a random effects model (RR = 1.27, 95% CI 1.18 to 1.36, I2 = 82.8%, p < .001). Additionally, the study showed a positive association between myocardial infraction (MI) and risk of all-cause cognitive impairment with a random effects model (RR = 1.49, 95% CI 1.20 to 1.84, I2 = 76.0%, p < .001). However, no significant association was detected between angina pectoris (AP) and risk of all-cause cognitive impairment with a random effects model (RR = 1.23, 95% CI 0.95 to 1.58, I2 = 79.1%, p < .001). Subgroup studies also showed that CHD patients are at higher risk for vascular dementia (VD), but not Alzheimer's disease (AD) (VD: RR = 1.34, 95% CI: 1.28-1.39; AD: RR = 0.99, 95% CI: 0.92-1.07).
Conclusion: In a word, CHD was significantly associated with an increased risk of developing cognitive impairment.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; coronary heart disease; dementia; meta-analysis.
© 2021 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest related to this study.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Association between Coronary Heart Disease, Heart Failure, and Risk of Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2023 Nov-Dec;26(6):958-965. doi: 10.4103/aian.aian_361_23. Epub 2023 Aug 25. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2023. PMID: 38229651 Free PMC article.
-
Coronary heart disease and risk for cognitive impairment or dementia: Systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 8;12(9):e0184244. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184244. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28886155 Free PMC article.
-
Renin-angiotensin system-targeting antihypertensive drugs and risk of vascular cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis.Neurosci Lett. 2016 Feb 26;615:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.01.011. Epub 2016 Jan 12. Neurosci Lett. 2016. PMID: 26797651
-
Associations between heart failure and risk of dementia: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Jan;99(5):e18492. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018492. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32000359 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of Lung Function Decline with Risks of Cognitive Impairment and Dementia: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review.J Alzheimers Dis. 2023;92(3):853-873. doi: 10.3233/JAD-221136. J Alzheimers Dis. 2023. PMID: 36806509
Cited by
-
Risk factors for cognitive dysfunction amongst patients with cardiovascular diseases.Front Public Health. 2024 Sep 13;12:1385089. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1385089. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39346594 Free PMC article.
-
Protecting vascular health: the role of flavonoids during pregnancy complications in mitigating the risk of vascular dementia later in life.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Jun;33(6):2919-2934. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01788-w. Epub 2025 Jun 5. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40471470 Review.
-
Association between Coronary Heart Disease, Heart Failure, and Risk of Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2023 Nov-Dec;26(6):958-965. doi: 10.4103/aian.aian_361_23. Epub 2023 Aug 25. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2023. PMID: 38229651 Free PMC article.
-
Attention as the primary cognitive domain affected in post-myocardial infarction cognitive impairment: a prospective multicenter study.Sci Rep. 2025 May 8;15(1):16025. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-00421-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40341432 Free PMC article.
-
Multimorbidity, cognitive phenotypes, and Alzheimer's disease plasma biomarkers in older adults: A population-based study.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Mar;20(3):1550-1561. doi: 10.1002/alz.13519. Epub 2023 Dec 2. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 38041805 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abete, P. , Della‐Morte, D. , Gargiulo, G. , Basile, C. , Langellotto, A. , Galizia, G. , Testa, G. , Canonico, V. , Bonaduce, D. , & Cacciatore, F. (2014). Cognitive impairment and cardiovascular diseases in the elderly. A heart‐brain continuum hypothesis. Ageing Research Reviews, 18, 41–52. 10.1016/j.arr.2014.07.003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ang, C. S. , & Chan, K. M. (2016). A review of coronary artery disease research in Malaysia. Medical Journal of Malaysia, 71(Suppl 1), 42–57. - PubMed
-
- Bleckwenn, M. , Kleineidam, L. , Wagner, M. , Jessen, F. , Weyerer, S. , Werle, J. , Wiese, B. , Lühmann, D. , Posselt, T. , König, H.‐H. , Brettschneider, C. , Mösch, E. , Weeg, D. , Fuchs, A. , Pentzek, M. , Luck, T. , Riedel‐Heller, S. G. , Maier, W. , & Scherer, M. (2017). Impact of coronary heart disease on cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease: A prospective longitudinal cohort study in primary care. British Journal of General Practice, 67(655), e111–e117. 10.3399/bjgp16X688813 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

