Efficient CRISPR/Cas9 mutagenesis for neurobehavioral screening in adult zebrafish
- PMID: 33742663
- PMCID: PMC8496216
- DOI: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab089
Efficient CRISPR/Cas9 mutagenesis for neurobehavioral screening in adult zebrafish
Abstract
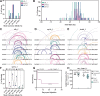
Adult zebrafish are widely used to interrogate mechanisms of disease development and tissue regeneration. Yet, the prospect of large-scale genetics in adult zebrafish has traditionally faced a host of biological and technical challenges, including inaccessibility of adult tissues to high-throughput phenotyping and the spatial and technical demands of adult husbandry. Here, we describe an experimental pipeline that combines high-efficiency CRISPR/Cas9 mutagenesis with functional phenotypic screening to identify genes required for spinal cord repair in adult zebrafish. Using CRISPR/Cas9 dual-guide ribonucleic proteins, we show selective and combinatorial mutagenesis of 17 genes at 28 target sites with efficiencies exceeding 85% in adult F0 "crispants". We find that capillary electrophoresis is a reliable method to measure indel frequencies. Using a quantifiable behavioral assay, we identify seven single- or duplicate-gene crispants with reduced functional recovery after spinal cord injury. To rule out off-target effects, we generate germline mutations that recapitulate the crispant regeneration phenotypes. This study provides a platform that combines high-efficiency somatic mutagenesis with a functional phenotypic readout to perform medium- to large-scale genetic studies in adult zebrafish.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; genetic screen; regeneration; spinal cord injury; zebrafish.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Genetics Society of America.
Figures





References
-
- Becker CG, Becker T.. 2015. Neuronal regeneration from ependymo-radial glial cells: cook, little pot, cook!. Dev Cell. 32:516–527. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
