The role of mGlu4 receptors within the nucleus accumbens in acquisition and expression of morphine-induced conditioned place preference in male rats
- PMID: 33743609
- PMCID: PMC7981834
- DOI: 10.1186/s12868-021-00627-2
The role of mGlu4 receptors within the nucleus accumbens in acquisition and expression of morphine-induced conditioned place preference in male rats
Abstract
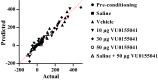
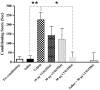
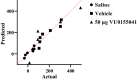
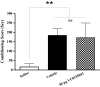
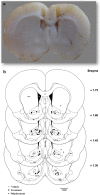
Background: Several studies have shown that glutamate neurotransmission in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) is required for the development of morphine-induced conditional place preference (CPP). In addition, metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) in NAc play important roles in the reward pathways. However, the precise role of mGluR4 in different steps of the morphine-induced CPP is less well known. In the present study the effect of bilateral intra-accumbal infusion of VU0155041, as a specific mGluR4 agonist on the acquisition and expression of morphine induced CPP in male Wistar rats was investigated. The animals were bilaterally implanted with guide cannulae above the NAc. In the first step of the study, the VU0155041 was administered at doses of 10, 30 and 50 μg/0.5 μL saline per side into the NAc during the 3 days of morphine (5 mg/kg) conditioning (acquisition) phase of morphine-induced CPP. In the second step of the study, the rats bilaterally received VU0155041 at the dose of 50 μg/0.5 μL, 5 min before the post-conditioning test in order to check the effect of VU0155041 on the expression of morphine-induced CPP.
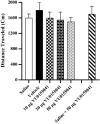
Results: The results showed that the intra-accumbal injection of VU0155041 inhibits the acquisition of morphine-induced CPP in a dose dependent manner, but had no effect on expression.
Conclusions: The data indicated that intra-NAc administration of VU0155041 dose dependently blocks the establishment of morphine-induced CPP and reduces the rewarding properties of morphine. These effects may be related to changes in glutamate activity in the NAC and/or learning dependent mechanism of glutamate neurotransmission in reward pathway(s).
Keywords: Conditioned place preference; Metabotropic glutamate receptor type 4; Morphine; Nucleus accumbens; Rat.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of the mGlu8 receptor agonist, (S)-3,4-DCPG on acquisition and expression of morphine-induced conditioned place preference in male rats.Behav Brain Funct. 2021 Feb 21;17(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12993-021-00174-0. Behav Brain Funct. 2021. PMID: 33612106 Free PMC article.
-
VU0155041, a positive allosteric modulator of mGluR4, in the nucleus accumbens facilitates extinction and inhibits the reinstatement of morphine-induced conditioned place preference in male rats.Brain Res Bull. 2023 Jun 1;197:57-64. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2023.03.012. Epub 2023 Mar 30. Brain Res Bull. 2023. PMID: 36997034
-
Intra-accumbal administration of AMN082, a metabotropic glutamate receptor type 7 allosteric agonist, inhibits the acquisition but not the expression of morphine-induced conditioned place preference in rats.Neurosci Lett. 2018 Aug 10;681:56-61. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.05.031. Epub 2018 May 22. Neurosci Lett. 2018. PMID: 29800675
-
Blockage of acquisition and expression of morphine-induced conditioned place preference in rats due to activation of glutamate receptors type II/III in nucleus accumbens.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2015 Aug;135:192-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2015.06.004. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2015. PMID: 26071679
-
The role of signaling molecules in reward-related incentive learning.Neurotox Res. 2004;6(1):91-104. doi: 10.1007/BF03033301. Neurotox Res. 2004. PMID: 15184110 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of intrahippocampal microinjection of VU0155041, a positive allosteric modulator of mGluR4, on long term potentiation in a valproic acid-induced autistic male rat model.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024 May 22;16:629-634. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2024.05.005. eCollection 2024 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38832089 Free PMC article.
-
Update on mGlu4 modulator patents: 2017 to present.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2025 May;35(5):463-475. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2025.2467679. Epub 2025 Feb 22. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2025. PMID: 39948693 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

