Neurobrucellosis with ischemic stroke and spinal cord involvement: a case report
- PMID: 33743640
- PMCID: PMC7980546
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-021-02155-2
Neurobrucellosis with ischemic stroke and spinal cord involvement: a case report
Abstract
Background: Brucellosis is a common zoonotic disease that may have a variety of clinical manifestations when it affects the nervous system. Ischemic stroke is a rare clinical symptom, but if it is not diagnosed and treated early, it may cause more severe consequences.
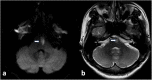
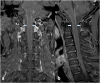
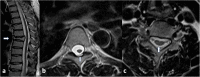
Case presentation: We report a 38-year-old man presenting with hearing impairment for four years and sudden weakness of the right limb for two years, recurrent aphasia, and gradual weakness of bilateral lower limbs for nine months. He had bilateral positive Babinski's sign. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) showed raised protein and pleocytosis. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed ischemic infarcts in the pons and extensive enhancement of spinal meninges combined with spinal cord atrophy and ischemia. The tests revealed Brucella Rose Bengal positive in serum and CSF. Brucella culture in CSF was also positive. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) of CSF revealed positive for Brucella with 105 species were detected. He showed significant improvement with antibiotics at five months follow-up.
Conclusions: Neurobrucellosis may mimic stroke and transverse myelitis like syndromes. NB is a treatable infectious condition and should always be considered in the differentials, especially if there are risk factors, as in our case.
Keywords: Cerebrospinal fluid; Neurobrucellosis; Spinal cord; Stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Case Report: Neurobrucellosis with Plastered Spinal Arachnoiditis: A Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Based Report.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2018 Mar;98(3):800-802. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.17-0828. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2018. PMID: 29345223 Free PMC article.
-
[A Case Report on Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Secondary to Neurobrucellosis in a Patient with Cerebral Aneurysm].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2023 Jul;57(3):481-489. doi: 10.5578/mb.20239940. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2023. PMID: 37462311 Turkish.
-
Neurobrucellosis: laboratory features, clinical characteristics, antibiotic treatment, and clinical outcomes of 21 patients.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 May 10;24(1):485. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09308-x. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38730327 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of early neurobrucellosis using metagenomic next-generation sequencing of the cerebrospinal fluid in nonepidemic zone: Case report and lecture review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Feb 14;104(7):e41481. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041481. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 39960952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brucellosis infection complicated with myelitis: a case report and literature review.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 May 16;14:1378331. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1378331. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38817447 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tissue infarction secondary to brucellosis: a systematic review of case reports and case series.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Feb 11;25(1):203. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10599-x. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39934661 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Karsen H, Koruk ST, Duygu F, Yapici K, Kati M. Review of 17 cases of neurobrucellosis: clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and management. Arch Iran Med. 2012;15:491–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

