State of the art in parallel ankle rehabilitation robot: a systematic review
- PMID: 33743757
- PMCID: PMC7981854
- DOI: 10.1186/s12984-021-00845-z
State of the art in parallel ankle rehabilitation robot: a systematic review
Abstract
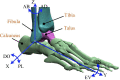
Background: The ankle joint complex (AJC) is of fundamental importance for balance, support, and propulsion. However, it is particularly susceptible to musculoskeletal and neurological injuries, especially neurological injuries such as drop foot following stroke. An important factor in ankle dysfunction is damage to the central nervous system (CNS). Correspondingly, the fundamental goal of rehabilitation training is to stimulate the reorganization and compensation of the CNS, and to promote the recovery of the motor system's motor perception function. Therefore, an increasing number of ankle rehabilitation robots have been developed to provide long-term accurate and uniform rehabilitation training of the AJC, among which the parallel ankle rehabilitation robot (PARR) is the most studied. The aim of this study is to provide a systematic review of the state of the art in PARR technology, with consideration of the mechanism configurations, actuator types with different trajectory tracking control techniques, and rehabilitation training methods, thus facilitating the development of new and improved PARRs as a next step towards obtaining clinical proof of their rehabilitation benefits.
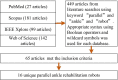
Methods: A literature search was conducted on PubMed, Scopus, IEEE Xplore, and Web of Science for articles related to the design and improvement of PARRs for ankle rehabilitation from each site's respective inception from January 1999 to September 2020 using the keywords " parallel", " ankle", and " robot". Appropriate syntax using Boolean operators and wildcard symbols was utilized for each database to include a wider range of articles that may have used alternate spellings or synonyms, and the references listed in relevant publications were further screened according to the inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria.
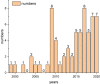
Results and discussion: Ultimately, 65 articles representing 16 unique PARRs were selected for review, all of which have developed the prototypes with experiments designed to verify their usability and feasibility. From the comparison among these PARRs, we found that there are three main considerations for the mechanical design and mechanism optimization of PARRs, the choice of two actuator types including pneumatic and electrically driven control, the covering of the AJC's motion space, and the optimization of the kinematic design, actuation design and structural design. The trajectory tracking accuracy and interactive control performance also need to be guaranteed to improve the effect of rehabilitation training and stimulate a patient's active participation. In addition, the parameters of the reviewed 16 PARRs are summarized in detail with their differences compared by using figures and tables in the order they appeared, showing their differences in the two main actuator types, four exercise modes, fifteen control strategies, etc., which revealed the future research trends related to the improvement of the PARRs.
Conclusion: The selected studies showed the rapid development of PARRs in terms of their mechanical designs, control strategies, and rehabilitation training methods over the last two decades. However, the existing PARRs all have their own pros and cons, and few of the developed devices have been subjected to clinical trials. Designing a PARR with three degrees of freedom (DOFs) and whereby the mechanism's rotation center coincides with the AJC rotation center is of vital importance in the mechanism design and optimization of PARRs. In addition, the design of actuators combining the advantages of the pneumatic-driven and electrically driven ones, as well as some new other actuators, will be a research hotspot for the development of PARRs. For the control strategy, compliance control with variable parameters should be further studied, with sEMG signal included to improve the real-time performance. Multimode rehabilitation training methods with multimodal motion intention recognition, real-time online detection and evaluation system should also be further developed to meet the needs of different ankle disability and rehabilitation stages. In addition, the clinical trials are in urgent need to help the PARRs be implementable as an intervention in clinical practice.
Keywords: Mechanism configurations; Parallel ankle rehabilitation robot; Rehabilitation training; Trajectory tracking control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Sammarco GJ. Rehabilitation of the foot and ankle. Missouri: Mosby-Year Book; 1995.
-
- Mozaffarian DB, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2015 Update: a report from the American heart association. Circulation. 2015;133(4):e38–360. - PubMed
-
- WHO, Atlas of heart disease and stroke. Geneva: WHO Press, 2011.
-
- Zhang M, Zhu G, Nandakumar A, et al. A virtual-reality tracking game for use in robot-assisted ankle rehabilitation. In: IEEE/ASME International Conference on Mechatronic & Embedded Systems & Applications (MESA), Senigallia. 2014, pp. 1-4.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

