DNASE1L3 arrests tumor angiogenesis by impairing the senescence-associated secretory phenotype in response to stress
- PMID: 33744849
- PMCID: PMC8064203
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.202740
DNASE1L3 arrests tumor angiogenesis by impairing the senescence-associated secretory phenotype in response to stress
Abstract
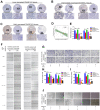
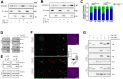
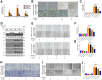
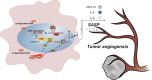
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most challenging and aggressive cancers with limited treatment options because of tumor heterogeneity. Tumor angiogenesis is a hallmark of HCC and is necessary for tumor growth and progression. DNA damage stress and its associated deoxyribonuclease1-like 3 (DNASE1L3) are involved in HCC progression. Here, we explored the influence mechanism of DNASE1L3 on tumor angiogenesis under DNA damage stress in vitro and in vivo. DNASE1L3 was found downregulated and negatively correlated with poor prognosis of resectable and unresectable HCC patients. The tissue microarray of HCC revealed the negative association between DNASE1L3 and cancer vasculature invasion. Mechanistically, DNASE1L3 was found to relieve cytoplasmic DNA accumulation under DNA damage stress in HCC cell lines, in turn cell senescence and senescence-associated secretory phenotype were arrested via the p53 and NF-κB signal pathway, and hence, tumor angiogenesis was impaired. Furthermore, we found that DNASE1L3 excised these functions by translocating to the nucleus and interacting with H2BE under DNA damage stress using co-immunoprecipitation and fluorescence resonance energy transfer assay. In conclusion, DNASE1L3 inhibits tumor angiogenesis via impairing the senescence-associated secretory phenotype in response to DNA damage stress.
Keywords: DNASE1L3; angiogenesis; hepatocellular carcinoma; senescence.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Abou-Alfa GK, Qin S, Ryoo BY, Lu SN, Yen CJ, Feng YH, Lim HY, Izzo F, Colombo M, Sarker D, Bolondi L, Vaccaro G, Harris WP, et al. Phase III randomized study of second line ADI-PEG 20 plus best supportive care versus placebo plus best supportive care in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Oncol. 2018; 29:1402–08. 10.1093/annonc/mdy101 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

