The fluoride transporter FLUORIDE EXPORTER (FEX) is the major mechanism of tolerance to fluoride toxicity in plants
- PMID: 33744970
- PMCID: PMC8195535
- DOI: 10.1093/plphys/kiab131
The fluoride transporter FLUORIDE EXPORTER (FEX) is the major mechanism of tolerance to fluoride toxicity in plants
Abstract
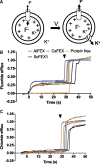
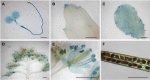
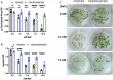
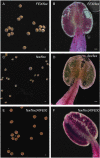
Fluoride is everywhere in the environment, yet it is toxic to living things. How biological organisms detoxify fluoride has been unknown until recently. Fluoride-specific ion transporters in both prokaryotes (Fluoride channel; Fluc) and fungi (Fluoride Exporter; FEX) efficiently export fluoride to the extracellular environment. FEX homologues have been identified throughout the plant kingdom. Understanding the function of FEX in a multicellular organism will reveal valuable knowledge about reducing toxic effects caused by fluoride. Here we demonstrate the conserved role of plant FEX (FLUORIDE EXPORTER) in conferring fluoride tolerance. Plant FEX facilitates the efflux of toxic fluoride ions from yeast cells and is required for fluoride tolerance in plants. A CRISPR/Cas9-generated mutation in Arabidopsis thaliana FEX renders the plant vulnerable to low concentrations (100 µM) of fluoride at every stage of development. Pollen is particularly affected, failing to develop even at extremely low levels of fluoride in the growth medium. The action of the FEX membrane transport protein is the major fluoride defense mechanism in plants.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures






References
-
- Agarwal M, Rai K, Shrivastav R, Dass S (2002) A study on fluoride sorption by montmorillonite and kaolinite. Water Air Soil Pollut 141: 247–261
-
- Anbuvel D, Kumaresan S, Margret RJ (2014) Fluoride analysis of soil in cultivated areas of Thovalai channel in Kanyakumari district, Tamil Nadu, India: correlation with physico-chemical parameters. Int J Basic Appl Chem Sci 4: 20–29
-
- Barnes JD, Balaguer L, Manrique E, Elvira S, Davison AW (1992) A reappraisal of the use of DMSO for the extraction and determination of chlorophylls a and b in lichens and higher plants. Environ Exp Bot 32: 85–100
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

