Regulator-dependent temporal dynamics of a restriction-modification system's gene expression upon entering new host cells: single-cell and population studies
- PMID: 33744971
- PMCID: PMC8053105
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkab183
Regulator-dependent temporal dynamics of a restriction-modification system's gene expression upon entering new host cells: single-cell and population studies
Abstract
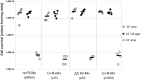
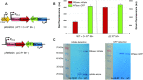
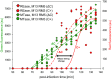
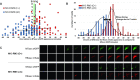
Restriction-modification (R-M) systems represent a first line of defense against invasive DNAs, such as bacteriophage DNAs, and are widespread among bacteria and archaea. By acquiring a Type II R-M system via horizontal gene transfer, the new hosts generally become more resistant to phage infection, through the action of a restriction endonuclease (REase), which cleaves DNA at or near specific sequences. A modification methyltransferase (MTase) serves to protect the host genome against its cognate REase activity. The production of R-M system components upon entering a new host cell must be finely tuned to confer protective methylation before the REase acts, to avoid host genome damage. Some type II R-M systems rely on a third component, the controller (C) protein, which is a transcription factor that regulates the production of REase and/or MTase. Previous studies have suggested C protein effects on the dynamics of expression of an R-M system during its establishment in a new host cell. Here, we directly examine these effects. By fluorescently labelling REase and MTase, we demonstrate that lack of a C protein reduces the delay of REase production, to the point of being simultaneous with, or even preceding, production of the MTase. Single molecule tracking suggests that a REase and a MTase employ different strategies for their target search within host cells, with the MTase spending much more time diffusing in proximity to the nucleoid than does the REase. This difference may partially ameliorate the toxic effects of premature REase expression.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

