Overview of the contemporary management of supracondylar humeral fractures in children
- PMID: 33744996
- PMCID: PMC8233294
- DOI: 10.1007/s00590-021-02932-2
Overview of the contemporary management of supracondylar humeral fractures in children
Abstract
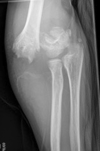
Purpose: Supracondylar fractures are common injuries accounting for approximately 15% of all fractures in children with a large body of literature on this subject.
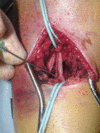
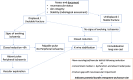
Methods: This article critically appraises the available evidence to provide an overview of the treatment options including the role and timing of surgery, the geometry of wire fixation and the management of nerve and arterial injury.
Conclusion: Management decisions are based on a number of considerations particularly fracture stability. Closed reduction and percutaneous K-wire stabilisation are commonly recommended for an unstable displaced fracture. These techniques are however associated with the potential for iatrogenic neurological injury. Vascular injury is also rare but must be recognised and treated promptly to avoid significant permanent morbidity.
Keywords: Cubitus Varus; Neurovascular; Review; Supracondylar; Treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
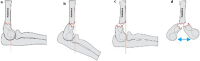
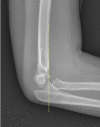
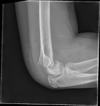
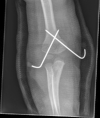
References
-
- Gartland JJ. Management of supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1959;109(2):145–154. - PubMed
-
- Cheng JC, Shen WY. Limb fracture pattern in different pediatric age groups: a study of 3350 children. J Orthop Trauma. 1993;7(1):15–22. - PubMed
-
- Cheng JC, Ng BK, Ying SY, et al. A 10-year study of the changes in the pattern and treatment of 6,493 fractures. J Pediatr Orthop. 1999;19(3):344–350. - PubMed
-
- Beaty JH and Kasser JR (2006) Rockwood and Wilkins’ Fracture in Children. 6th Edition, Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

