Remifentanil provides an increased proportion of time under light sedation than fentanyl when combined with dexmedetomidine for mechanical ventilation
- PMID: 33745360
- PMCID: PMC7989131
- DOI: 10.1177/03000605211002683
Remifentanil provides an increased proportion of time under light sedation than fentanyl when combined with dexmedetomidine for mechanical ventilation
Abstract
Objective: To compare the effects of remifentanil versus fentanyl during light sedation with dexmedetomidine in adults receiving mechanical ventilation (MV) in the intensive care unit.
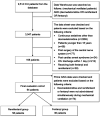
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, we compared the use of remifentanil versus fentanyl in adults receiving MV with dexmedetomidine sedation. The primary outcome was the proportion of time under light sedation (Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale score between -1 and 0) during MV.
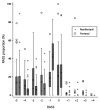
Results: We included 94 patients and classified 58 into the remifentanil group and 36 into the fentanyl group. The mean proportion of time under light sedation during MV was 66.6% ± 18.5% in the remifentanil group and 39.9% ± 27.3% in the fentanyl group. In the multivariate analysis with control for confounding factors, patients in the remifentanil group showed a significantly higher proportion of time under light sedation than patients in the fentanyl group (mean difference: 24.3 percentage points; 95% confidence interval: 12.9-35.8).
Conclusions: Remifentanil use might increase the proportion of time under light sedation in patients receiving MV compared with fentanyl administration.
Keywords: Light sedation; dexmedetomidine; fentanyl; mechanical ventilation; opioid; remifentanil.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Devlin JW, Skrobik Y, Gélinas C, et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Pain, Agitation/Sedation, Delirium, Immobility, and Sleep Disruption in Adult Patients in the ICU. Crit Care Med 2018; 46: e825–e873. - PubMed
-
- Romagnoli S, Amigoni A, Blangetti I, et al . Light sedation with dexmedetomidine: a practical approach for the intensivist in different ICU patients. Minerva Anestesiol 2018; 84: 731–746. - PubMed
-
- Shehabi Y, Howe BD, Bellomo R, et al. Early Sedation with Dexmedetomidine in Critically Ill Patients. N Engl J Med 2019; 380: 2506–2517. - PubMed
-
- Rosow CE. An overview of remifentanil. Anesth Analg 1999; 89: S1–S3. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

