The Molecular Context of Vulnerability for CDK9 Suppression in Triple Wild-Type Melanoma
- PMID: 33745909
- PMCID: PMC8316294
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jid.2020.12.035
The Molecular Context of Vulnerability for CDK9 Suppression in Triple Wild-Type Melanoma
Abstract
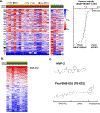
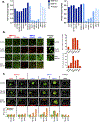
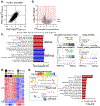
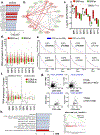
Approximately half of melanoma tumors lack a druggable target and are unresponsive to current targeted therapeutics. One proposed approach for treating these therapeutically orphaned tumors is by targeting transcriptional dependencies (oncogene starvation), whereby survival factors are depleted through inhibition of transcriptional regulators. A drug screen identified a CDK9 inhibitor (SNS-032) to have therapeutic selectivity against wild-type (wt) BRAFwt/NRASwt melanomas compared with BRAFmut/NRASmut mutated melanomas. We then used two strategies to inhibit CDK9 in vitro-a CDK9 degrader (TS-032) and a selective CDK9 kinase inhibitor (NVP-2). At 500 nM, both TS-032 and NVP-2 demonstrated greater suppression of BRAFwt/NRASwt/NF1wt cutaneous and uveal melanomas than mutant melanomas. RNA sequencing analysis of eight melanoma lines with NVP-2 treatment demonstrated that the context of this vulnerability appears to converge on a cell cycle network that includes many transcriptional regulators, such as the E2F family members. The Cancer Genome Atlas human melanoma tumor data further supported a potential oncogenic role for E2F1 and E2F2 in BRAFwt/NRASwt/NF1wt tumors and a direct link to CDK9. Our results suggest that transcriptional blockade through selective targeting of CDK9 is an effective method of suppressing therapeutically orphaned BRAF/NRAS/NF1 wt melanomas.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Alla V, Engelmann D, Niemetz A, Pahnke J, Schmidt A, Kunz M, et al. E2F1 in melanoma progression and metastasis. J Natl Cancer Inst 2010;102(2):127–33. - PubMed
-
- Brahmer JR, Drake CG, Wollner I, Powderly JD, Picus J, Sharfman WH, et al. Phase I study of single-agent anti-programmed death-1 (MDX-1106) in refractory solid tumors: safety, clinical activity, pharmacodynamics, and immunologic correlates. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2010;28(19):3167–75. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

