Definition and management of invasive fungal rhinosinusitis: a single-centre retrospective study
- PMID: 33746222
- PMCID: PMC7982758
- DOI: 10.14639/0392-100X-N0848
Definition and management of invasive fungal rhinosinusitis: a single-centre retrospective study
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to correlate acute invasive fungal rhinosinusitis (AIFRS) and chronic invasive fungal rhinosinusitis with underlying diseases, aetiological microorganisms, clinical symptoms, radiological findings, and surgical and medical treatment to determine the subset of patients who require more accurate diagnostic investigation and to prevent irreversible complications.
Methods: This retrospective monocentric study included 17 patients who underwent endoscopic sinus surgery evaluated by paranasal computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Age, sex and symptoms, and location of the invasive fungal infection and the causative fungus were analysed.
Results: In total, 4 patients were affected by the AIFRS form, and 13 by the chronic form. Diabetes mellitus was reported in 41.17% of cases, and haematological diseases in 23.52%. The maxillary sinuses were involved in 47.05% of cases and sphenoidal sinuses in 52.94%; Aspergillus fumigatus was the fungus in 76.47% of cases, and Zygomycetes in 23.53%.
Conclusions: An understanding of the different types of fungal sinusitis and knowledge of their features play a crucial role in reaching prompt diagnosis and initiation of appropriate therapy, which is essential to avoid a protracted or fatal outcome.
Definizione e gestione della rinosinusite fungina invasiva: uno studio retrospettivo monocentrico.
Obiettivi: Nonostante i progressi in termini di trattamento, la mortalità nei casi di rinosinusite fungina invasiva rimane elevata, pertanto, scopo dello studio è stato correlare le forme acute invasive e quelle croniche con patologie concomitanti, agenti eziologici, i sintomi clinici, radiologia e trattamento, al fine di identificare e trattare i pazienti con prognosi peggiore.
Metodi: Il seguente studio retrospettivo monocentrico ha incluso 17 pazienti sottoposti a chirurgia endoscopica sinusale, valutati mediante TC e RM e analizzati per età, sesso, sintomi, sede dell’infezione fungina invasiva e microrganismi eziologici.
Risultati: 4 pazienti sono risultati affetti dalla forma invasiva acuta,13 pazienti dalla forma cronica. Il diabete mellito è stato riscontrato nel 41,17% dei casi, malattie ematologiche nel 23,52%. I seni mascellari sono risultati coinvolti nel 47,05% dei pazienti e seni sfenoidali nel 52,94%; Aspergillus ha provocato il 76,47% dei casi, Zigomiceti il 23,53%.
Conclusioni: Un’adeguata comprensione dei diversi tipi di sinusite fungina e la conoscenza delle loro caratteristiche svolgono un ruolo cruciale ai fini di una diagnosi precoce e l’avvio di una terapia appropriata con lo scopo di ridurne la mortalità.
Keywords: Aspergillus; Mucormycosis; invasive fungal rhinosinusitis; isavuconazole; liposomal amphotericin B.
Copyright © 2021 Società Italiana di Otorinolaringoiatria e Chirurgia Cervico-Facciale, Rome, Italy.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

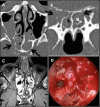
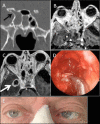
Similar articles
-
Fungal rhinosinusitis.Prilozi. 2012;33(1):187-97. Prilozi. 2012. PMID: 22952104
-
Prognosis of acute invasive fungal rhinosinusitis related to underlying disease.Int J Infect Dis. 2011 Dec;15(12):e841-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2011.08.005. Epub 2011 Oct 2. Int J Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21963345
-
Acute invasive fungal rhinosinusitis: our experience in immunocompromised host.Mymensingh Med J. 2013 Oct;22(4):814-9. Mymensingh Med J. 2013. PMID: 24292316
-
Fungal Rhinosinusitis: A Radiological Review With Intraoperative Correlation.Can Assoc Radiol J. 2017 May;68(2):178-186. doi: 10.1016/j.carj.2016.12.009. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2017. PMID: 28438285 Review.
-
Successful Isavuconazole therapy in a patient with acute invasive fungal rhinosinusitis and acquired immune deficiency syndrome.Am J Otolaryngol. 2016 Mar-Apr;37(2):152-5. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2015.12.003. Epub 2015 Dec 9. Am J Otolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 26954873 Review.
Cited by
-
Invasive Fungal Rhinosinusitis: The First Histopathological Study in Vietnam.Head Neck Pathol. 2024 Oct 16;18(1):104. doi: 10.1007/s12105-024-01711-9. Head Neck Pathol. 2024. PMID: 39412604
-
Invasive Sinusitis Presenting with Orbital Complications in COVID Patients: Is Mucor the Only Cause?Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024 Feb;76(1):55-63. doi: 10.1007/s12070-023-04077-6. Epub 2023 Jul 28. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024. PMID: 38440575 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19-Associated Mucormycosis, A New Incident in Recent Time: Is An Emerging Disease in The Near Future Impending?Avicenna J Med. 2021 Dec 2;11(4):210-216. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1735383. eCollection 2021 Oct. Avicenna J Med. 2021. PMID: 34881204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinicopathological and microbiological study of fungal rhinosinusitis treated with endoscopic surgery.Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2025 Apr;45(2):100-109. doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-N2808. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2025. PMID: 39844757 Free PMC article.
-
Postoperative Recurrence in Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis: A Single Center Experience.Cureus. 2025 Apr 4;17(4):e81711. doi: 10.7759/cureus.81711. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40330364 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ergun O, Tahir E, Kuscu CO, et al. . Acute invasive fungal rhinosinusitis: Presentation of 19 cases, review of the literature and a new classification system. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2016;75:767.e1-e9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2016.11.004 10.1016/j.joms.2016.11.004 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Montone KT. Pathology of fungal rhinosinusitis: a review. Head Neck Pathol 2016;10:40-6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12105-016-0690-0 10.1007/s12105-016-0690-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Deutsch PG, Whittaker J, Prasad S. Invasive and non-invasive fungal rhinosinusitis – a review and update of the evidence. Medicina (Kaunas) 2019;55:319. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55070319 10.3390/medicina55070319 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Trief D, Gray ST, Jakobie C, et al. . Invasive fungal disease of the sinus and orbit: a comparison between mucormycosis and Aspergillus. J Ophthalmol 2016;100:184-8. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjophthalmol-2015-306945 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2015-306945 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Duggal P, Wise SK. Invasive fungal rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy 2013;27(Suppl 1):S28-30. https://doi.org/10.2500/ajra.2013.27.3892 10.2500/ajra.2013.27.3892 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

