Genotyping and phylogenetic analysis of hydatid cysts isolated from livestock in Bushehr province, Iran
- PMID: 33746404
- PMCID: PMC7921263
- DOI: 10.1007/s12639-020-01293-7
Genotyping and phylogenetic analysis of hydatid cysts isolated from livestock in Bushehr province, Iran
Abstract
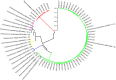
Hydatid cyst is one of the parasitic zoonoses caused by infection with the larval stage of Echinococcus granulosus tapeworm. The spread of this parasite is global and is of great importance in terms of public health. To date, ten different species of this parasite have been identified that differ in characteristics such as life cycle, epidemiology and pathogenesis. The purpose of this study was to determine the genotype and phylogenetic relationship of hydatid cysts isolated from livestock of Bushehr province, Iran. About 62 samples of hepatic and pulmonary hydatid cysts were collected from slaughtered animals. DNA extracted by phenol-chloroform method was amplified by PCR using primers specific for the cox1 gene. The PCR products of 50 samples were sequenced and analyzed using BioEdit software and compared with sequences in the GenBank. The phylogenetic tree was drawn using Neighbor Joining tree-NJ method, and its reliability was evaluated. Sequencing results showed that out of 50 sequenced samples, 43 samples had the genotype of Echinococcus granulosus and 7 samples had the genotype of Taenia hydatigena. By drawing a phylogenetic tree, all 43 hydatid cyst samples belonged to G1 strain. The predominance of G1 strain of hydatid cyst in livestock of Bushehr province shows the main role of this genotype in establishing the life cycle of parasite in this region and if the genotype of the parasite in dogs and humans is determined, then these findings can be used to disrupt the life cycle of the parasite and reduce the human infections.
Keywords: Bushehr province; Echinococcus granulosus; Genotype; Hydatid cyst.
© Indian Society for Parasitology 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abbas IE, Al-Kappany YM, Al-Araby MA. Prevalence and molecular characterization of hydatid cyst isolates from cattle in Egypt. Asian J Anim Vet Adv. 2016;11:794–804. doi: 10.3923/ajava.2016.794.804. - DOI
-
- Alvi MA, Ohiolei JA, Saqib M, Li L, Muhammad N, Tayyab MH, Qamar W, Alvi AA, Wu YD, Li XR, Fu BQ. Preliminary information on the prevalence and molecular description of Taenia hydatigena isolates in Pakistan based on mitochondrial cox1 gene. Infect Genet Evol. 2020;28:104481. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104481. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
