Therapeutic Effectiveness of AxioBionics Wearable Therapy Pain Management System in Patients with Chronic Lower Back Pain
- PMID: 33746519
- PMCID: PMC7903834
- DOI: 10.1177/1179544121993778
Therapeutic Effectiveness of AxioBionics Wearable Therapy Pain Management System in Patients with Chronic Lower Back Pain
Abstract
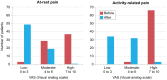
Chronic lower back pain is one of the most common medical conditions leading to a significant decrease in quality of life. This study retrospectively analyzed whether the AxioBionics Wearable Therapy Pain Management (WTPM) System, a customized and wearable electrical stimulation device, alleviated chronic lower back pain, and improved muscular function. This study assessed self-reported pain levels using the visual analog scale before and during the use of the AxioBionics WTPM System when performing normal activities such as sitting, standing, and walking (n = 69). Results showed that both at-rest and activity-related pain were significantly reduced during treatment with the AxioBionics WTPM System (% reduction in pain: 64% and 60%, respectively; P < .05). Thus, this study suggests that the AxioBionics WTPM System is efficacious in treating chronic lower back pain even when other therapies have failed to sufficiently decrease reported pain levels.
Keywords: AxioBionics WTPM system; Lower back pain; wearable therapy pain management system.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests:The author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: Philip Muccio is an owner of Axiobionics, LLC Josh Schueller is employed by Axiobionics, LLC Norm Howe is a paid consultant to Axiobioncs, LLC Miriam van Emde Boas did not receive remuneration for her contribution to the paper Edward Dabrowski did not receive remuneration for his contribution to the paper David Durrant did not receive remuneration for his contribution to the paper
Figures







References
-
- National Center for Health Statistics (US). Health, United States, 2006: With Chartbook on Trends in the Health of Americans. National Center for Health Statistics (US); 2006. - PubMed
-
- Luo X, Pietrobon R, Sun SX, Liu GG, Hey L. Estimates and patterns of direct health care expenditures among individuals with back pain in the United States. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29:79-86. - PubMed
-
- Stewart WF, Ricci JA, Chee E, Morganstein D, Lipton R. Lost productive time and cost due to common pain conditions in the US workforce. JAMA. 2003;290:2443-2454. - PubMed
-
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Advancing Pain Research, Care, and Education. Relieving Pain in America: A Blueprint for Transforming Prevention, Care, Education, and Research. (presentation). 2020. Updated 2020. Accessed July 4, 2020 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK91497/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK91497.pdf
-
- Institute of Medicine; Board on Health Sciences Policy; Committee on Advancing Pain Research, Care, and Education. Relieving Pain in America: A Blueprint for Transforming Prevention, Care, Education, and Research. The National Academies Press (US); 2011. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

