Transporter-mediated ecdysteroid trafficking across cell membranes: A novel target for insect growth regulators
- PMID: 33746543
- PMCID: PMC7953032
- DOI: 10.1584/jpestics.D20-071
Transporter-mediated ecdysteroid trafficking across cell membranes: A novel target for insect growth regulators
Abstract
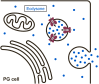
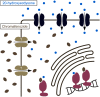
Ecdysteroids are a class of steroid hormones in arthropods that control molting and metamorphosis through interaction with intracellular nuclear receptors. In contrast to the extensive literature describing their biosynthetic pathways and signaling components, little has been known about how these hormones are traveling into and out of the cells through lipid bilayers of the cell membranes. Recently, a series of studies conducted in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster revealed that membrane transporters have critical functions in trafficking ecdysteroids across cell membranes, challenging the classical simple diffusion model of steroid hormone transport. Here we summarize recent advances in our understanding of membrane transporters involved in ecdysteroid signaling in Drosophila, with particular focus on Ecdysone Importer (EcI) that is involved in ecdysteroid uptake in peripheral tissues. We then discuss the potential advantage of EcI blockers as a novel pest management tool as compared to classical insect growth regulators.
Keywords: EcR; Ecdysone Importer; IGR; ecdysone; ecdysteroid.
© Pesticide Science Society of Japan 2021. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rapid Assessment of Insect Steroid Hormone Entry Into Cultured Cells.Front Physiol. 2022 Jan 26;12:816058. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.816058. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35145429 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of candidate intermediates in the Black Box of the ecdysone biosynthetic pathway in Drosophila melanogaster: Evaluation of molting activities on ecdysteroid-defective larvae.J Insect Physiol. 2016 Oct-Nov;93-94:94-104. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2016.09.012. Epub 2016 Sep 20. J Insect Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27662806
-
A Membrane Transporter Is Required for Steroid Hormone Uptake in Drosophila.Dev Cell. 2018 Nov 5;47(3):294-305.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2018.09.012. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Dev Cell. 2018. PMID: 30293839 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress in understanding the role of ecdysteroids in adult insects: Germline development and circadian clock in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster.Zoological Lett. 2015 Nov 2;1:32. doi: 10.1186/s40851-015-0031-2. eCollection 2015. Zoological Lett. 2015. PMID: 26605077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Compounds Inhibiting Noppera-bo, a Glutathione S-transferase Involved in Insect Ecdysteroid Biosynthesis: Novel Insect Growth Regulators.Biomolecules. 2023 Mar 2;13(3):461. doi: 10.3390/biom13030461. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36979396 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New ways and new hopes for IGR development.J Pestic Sci. 2021 Feb 20;46(1):3-6. doi: 10.1584/jpestics.M21-03. J Pestic Sci. 2021. PMID: 33746540 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Assessment of Insect Steroid Hormone Entry Into Cultured Cells.Front Physiol. 2022 Jan 26;12:816058. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.816058. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35145429 Free PMC article.
References
-
- S. Kopeć: Studies on the necessity of the brain for the inception of insect metamorphosis. Biol. Bull. 42, 323–342 (1922).
-
- J. W. Truman: The evolution of insect metamorphosis. Curr. Biol. 29, R1252–R1268 (2019). - PubMed
-
- A. Butenandt and P. Karlson: Über die isolierung eines metamorphose-hormons der insekten in kristallisierter form. Z. Naturforsch. B 9b, 389–391 (1954).
-
- D. L. Mykles: Ecdysteroid metabolism in crustaceans. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 127, 196–203 (2011). - PubMed
-
- R. Lafont, C. Dauphin-Villemant, J. T. Warren and H. Rees: Ecdysteroid chemistry and biochemistry. In “Insect Endocrinology,” ed. by L. I. Gilbert, Academic Press, London, pp. 106–176, 2012.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

