Identification of novel juvenile-hormone signaling activators via high-throughput screening with a chemical library
- PMID: 33746546
- PMCID: PMC7953030
- DOI: 10.1584/jpestics.D20-070
Identification of novel juvenile-hormone signaling activators via high-throughput screening with a chemical library
Abstract
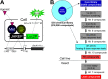
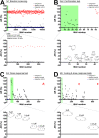
Juvenile hormone (JH) is an insect-specific hormone that regulates molting and metamorphosis. Hence, JH signaling inhibitors (JHSIs) and activators (JHSAs) can be used as effective insect growth regulators (IGRs) for pest management. In our previous study, we established a high-throughput screening (HTS) system for exploration of novel JHSIs and JHSAs using a Bombyx mori cell line (BmN_JF&AR cells) and succeeded in identifying novel JHSIs from a chemical library. Here, we searched for novel JHSAs using this system. The four-step HTS yielded 10 compounds as candidate JHSAs; some of these compounds showed novel basic structures, whereas the others were composed of a 4-phenoxyphenoxymethyl skeleton, the basic structure of several existing JH analogs (pyriproxyfen and fenoxycarb). Topical application of seven compounds to B. mori larvae significantly prolonged the larval period, suggesting that the identified JHSAs may be promising IGRs targeting the JH signaling pathway.
Keywords: high-throughput screening; insect growth regulator; juvenile hormone; juvenile hormone signaling activator; pest management.
© Pesticide Science Society of Japan 2021. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of a juvenile-hormone signaling inhibitor via high-throughput screening of a chemical library.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 27;10(1):18413. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-75386-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33110116 Free PMC article.
-
In silico and bio assay of juvenile hormone analogs as an insect growth regulator against Galleria mellonella (wax moth) - Part I.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2016 May;34(5):1061-78. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2015.1056549. Epub 2016 Apr 12. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2016. PMID: 27070862
-
The FOXO transcription factor controls insect growth and development by regulating juvenile hormone degradation in the silkworm, Bombyx mori.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jul 14;292(28):11659-11669. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.777797. Epub 2017 May 10. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28490635 Free PMC article.
-
The juvenile hormone receptor as a target of juvenoid "insect growth regulators".Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2020 Mar;103(3):e21615. doi: 10.1002/arch.21615. Epub 2019 Sep 10. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31502704 Review.
-
Hormonal regulation of insect metamorphosis with special reference to juvenile hormone biosynthesis.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2013;103:73-100. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385979-2.00003-4. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23347516 Review.
Cited by
-
New ways and new hopes for IGR development.J Pestic Sci. 2021 Feb 20;46(1):3-6. doi: 10.1584/jpestics.M21-03. J Pestic Sci. 2021. PMID: 33746540 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of insect hormone agonists.J Pestic Sci. 2024 Nov 20;49(4):303-310. doi: 10.1584/jpestics.J24-02. J Pestic Sci. 2024. PMID: 39877879 Free PMC article.
References
-
- L. M. Riddiford: Cellular and molecular actions of Juvenile hormone I. General considerations and premetamorphic actions. Adv. Insect Physiol. 24, 213–274 (1994).
-
- G. B. Staal: Insect growth regulators with juvenile hormone activity. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 20, 417–460 (1975). - PubMed
-
- C. Minakuchi and L. M. Riddiford: Insect juvenile hormone action as a potential target of pest management. J. Pestic. Sci. 31, 77–84 (2006).
-
- M. Jindra and L. Bittova: The juvenile hormone receptor as a target of juvenoid “insect growth regulators”. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 103, e21615 (2019). - PubMed
-
- A. R. Horowitz, M. Ghanim, E. Roditakis, R. Nauen and I. Ishaaya: Insecticide resistance and its management in Bemisia tabaci species. J. Pestic. Sci. 93, 893–910 (2020).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

