Qingda granule exerts neuroprotective effects against ischemia/reperfusion-induced cerebral injury via lncRNA GAS5/miR-137 signaling pathway
- PMID: 33746585
- PMCID: PMC7976574
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.53603
Qingda granule exerts neuroprotective effects against ischemia/reperfusion-induced cerebral injury via lncRNA GAS5/miR-137 signaling pathway
Abstract
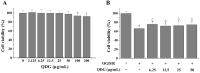
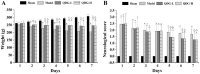
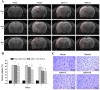
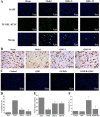
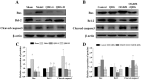
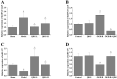
Background: Ischemic stroke is the second leading cause of death and disability worldwide, which needs to develop new pharmaceuticals for its prevention and treatment. Qingda granule (QDG), a traditional Chinese medicine formulation, could improve angiotensin II-induced brain injury and decrease systemic inflammation. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the neuroprotective effect of QDG against ischemia/reperfusion-induced cerebral injury and illustrate the potential mechanisms. Methods: The middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion (MCAO/R) surgery in vivo and oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R) in vitro models were established. Ischemic infarct volume was quantified using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Neurobehavioral deficits were assessed using a five-point scale. Cerebral histopathology was determined by hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining. Neuronal apoptosis was evaluated by TUNEL and immunostaining with NeuN antibodies. The protective effect of QDG on OGD/R-injured HT22 cells was determined by MTT assay and Hoechst 33258 staining. The expression of lncRNA GAS5, miR-137 and apoptosis-related proteins were investigated in MCAO/R-injured rats and in OGD/R-injured HT22 cells using RT-qPCR and western blot analysis. Results: QDG significantly reduced the ischemic infarct volume, which was accompanied with improvements in neurobehavioral deficits. Additionally, QDG significantly ameliorated cerebral histopathological changes and reduced neuron loss in MCAO/R-injured rats. Moreover, QDG improved growth and inhibited apoptosis of HT22 cells injured by OGD/R in vitro. Finally, QDG significantly decreased the expression of lncRNA GAS5, Bax and cleaved caspase3, whereas it increased miR-137 and Bcl-2 expression in MCAO/R-injured rats and in OGD/R-injured HT22 cells. Conclusion: QDG plays a neuroprotective role in ischemic stroke via regulation of the lncRNA GAS5/miR-137 signaling pathway.
Keywords: Qingda granule; ischemic stroke; lncRNA GAS5; miR-137; neuronal apoptosis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Qingda Granules alleviate brain damage in spontaneously hypertensive rats by modulating the miR-124/STAT3 signaling axis.Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025 Jan 20;45(1):18-26. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.03. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025. PMID: 39819708 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Rhein attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via inhibition of ferroptosis through NRF2/SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway.Exp Neurol. 2023 Nov;369:114541. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2023.114541. Epub 2023 Sep 14. Exp Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37714424
-
Xiaoxuming decoction enhanced neuroprotection after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion via the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway based on UPLC/HRMS, network pharmacology and experimental validation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jan 31;340:119279. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.119279. Epub 2024 Dec 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39725365
-
Neuroprotective and Anti-inflammatory Dual-Phenotypic Drug Screening Strategies.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2025 May 7;16(9):1631-1633. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5c00123. Epub 2025 Apr 10. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40208697 Review.
-
Tanshinone IIA Against Cerebral Ischemic Stroke and Ischemia- Reperfusion Injury: A Review of the Current Documents.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024;24(18):1701-1709. doi: 10.2174/0113895575299721240227070032. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38482618 Review.
Cited by
-
Network Pharmacology and Bioinformatics Methods Reveal the Mechanism of Berberine in the Treatment of Ischaemic Stroke.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jun 29;2022:5160329. doi: 10.1155/2022/5160329. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35815278 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of MiR-188-5p Downregulates IL6ST/STAT3/ NLRP3 Pathway to Ameliorate Neuron Injury in Oxygen-glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2024;21(3):263-273. doi: 10.2174/0115672026313555240515103132. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2024. PMID: 38778610
-
Ras-related protein Rab-20 inhibition alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting mitochondrial fission and dysfunction.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Oct 25;15:986710. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.986710. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36385754 Free PMC article.
-
Qingda Granule Attenuates Angiotensin II-Induced Renal Apoptosis and Activation of the p53 Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 10;12:770863. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.770863. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35222007 Free PMC article.
-
Qingda Granules alleviate brain damage in spontaneously hypertensive rats by modulating the miR-124/STAT3 signaling axis.Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025 Jan 20;45(1):18-26. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.03. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025. PMID: 39819708 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control, Prevention (CDC). Prevalence of stroke - United States, 2006-2010. MMWR-Morbid Mortal W. 2012;61:379–382. - PubMed
-
- Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM. New directions for protecting the heart against ischaemia-reperfusion injury: targeting the reperfusion injury salvage kinase (RISK)-pathway. Cardiovasc Res. 2004;61:448–460. - PubMed
-
- Brouns R, De Deyn PP. The complexity of neurobiological processes in acute ischemic stroke. Clin Neurol Neurosur. 2009;111:483–495. - PubMed
-
- Lei B, Popp S, Capuano Waters C, Cottrell JE, Kass IS. Lidocaine attenuates apoptosis in the ischemic penumbra and reduces infarct size after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Neuroscience. 2004;125:691–701. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

