HTRA1 Variants and the Interaction with Smoking Confer the Genetic Susceptibility to Ischemic Stroke
- PMID: 33746601
- PMCID: PMC7976583
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.45856
HTRA1 Variants and the Interaction with Smoking Confer the Genetic Susceptibility to Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
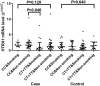
High temperature requirement protein A1 (HtrA1) was identified as the causative gene of autosomal recessive arteriopathy and associated with lacunar ischemic stroke (IS) in European. This study aimed at evaluating the association of HTRA1 with IS and four tagging single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were genotyped in a cohort of 4,098 Chinese. The mRNA level of HTRA1 in 72 IS cases and 72 hypertension controls were measured and compared. In whole population, SNP rs2268350 (C>T) was significantly associated with IS incidence (P=0.034). Stratification analysis observed significant association of rs2268350 in male, smoking and drinking populations, rs2672587 (C>G) in smoking and nonsmoking populations and rs3793917 (C>G) in smoking, nonsmoking and nondrinking populations with stroke respectively (P<0.05). The additive interaction and multiplicative interaction between rs2268350 and smoking were both of significant (P<0.05) after adjustment for the covariates. There was a cumulated risk of IS among genotypes of rs3793917 (P=0.009) and rs2672587 (P=0.047) in smoking population. The mRNA level of HTRA1 in non-smokers with rs2268350 CC was significantly higher than smokers with rs2268350 CT/TT (P=0.046) in IS cases. Our findings support that HTRA1 confers the genetic susceptibility to IS and smoking might modify the genetic effect of HTRA1 on IS by suppressing HTRA1 mRNA expression.
Keywords: HTRA1; interaction; ischemic stroke; mRNA.; smoking.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Donnan GA, Fisher M, Macleod M, Davis SM. Stroke. Lancet. 2008;371:1612–23. - PubMed
-
- Chen Z, Jiang B, Ru X, Sun H, Sun D, Liu X. et al. Mortality of Stroke and Its Subtypes in China: Results from a Nationwide Population-Based Survey. Neuroepidemiology. 2017;48:95–102. - PubMed
-
- Thrift AG, Dewey HM, Macdonell RA, McNeil JJ, Donnan GA. Incidence of the major stroke subtypes: initial findings from the North East Melbourne stroke incidence study (NEMESIS) Stroke. 2001;32:1732–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical