The Membrane Interaction of Alpha-Synuclein
- PMID: 33746714
- PMCID: PMC7969880
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2021.633727
The Membrane Interaction of Alpha-Synuclein
Abstract
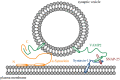
A presynaptic protein closely related to Parkinson's disease (PD), α-synuclein (α-Syn), has been studied extensively regarding its pathogenic mechanisms. As a physiological protein in presynapses, however, α-Syn's physiological function remains unclear. Its location in nerve terminals and effects on membrane fusion also imply its functional role in synaptic transmission, including its possible interaction with high-curvature membranes via its N-terminus and amorphous C-terminus. PD-related mutants that disrupt the membrane interaction (e.g., A30P and G51D) additionally suggest a relationship between α-Syn's pathogenic mechanisms and physiological roles through the membrane binding. Here, we summarize recent research on how α-Syn and its variants interact with membranes and influence synaptic transmission. We list several membrane-related connections between the protein's physiological function and the pathological mechanisms that stand to expand current understandings of α-Syn.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease; SNAREs; alpha-synuclein; membrane; synaptic transmission.
Copyright © 2021 Liu, Zhao, Xi, Jiang, Yu and Dong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous