The Theta Rhythm of the Hippocampus: From Neuronal and Circuit Mechanisms to Behavior
- PMID: 33746716
- PMCID: PMC7970048
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2021.649262
The Theta Rhythm of the Hippocampus: From Neuronal and Circuit Mechanisms to Behavior
Abstract
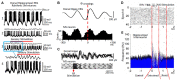
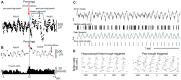
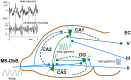
This review focuses on the neuronal and circuit mechanisms involved in the generation of the theta (θ) rhythm and of its participation in behavior. Data have accumulated indicating that θ arises from interactions between medial septum-diagonal band of Broca (MS-DbB) and intra-hippocampal circuits. The intrinsic properties of MS-DbB and hippocampal neurons have also been shown to play a key role in θ generation. A growing number of studies suggest that θ may represent a timing mechanism to temporally organize movement sequences, memory encoding, or planned trajectories for spatial navigation. To accomplish those functions, θ and gamma (γ) oscillations interact during the awake state and REM sleep, which are considered to be critical for learning and memory processes. Further, we discuss that the loss of this interaction is at the base of various neurophatological conditions.
Keywords: NMDA; cholinergic input; diagonal band of Broca; gamma oscillations; hippocampal neurons; medial septum.
Copyright © 2021 Nuñez and Buño.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Glutamatergic neurons of the mouse medial septum and diagonal band of Broca synaptically drive hippocampal pyramidal cells: relevance for hippocampal theta rhythm.J Neurosci. 2010 Nov 24;30(47):15951-61. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3663-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21106833 Free PMC article.
-
Interconnection and synchronization of neuronal populations in the mouse medial septum/diagonal band of Broca.J Neurophysiol. 2015 Feb 1;113(3):971-80. doi: 10.1152/jn.00367.2014. Epub 2014 Nov 12. J Neurophysiol. 2015. PMID: 25392162 Free PMC article.
-
Optogenetic Activation of Septal Glutamatergic Neurons Drive Hippocampal Theta Rhythms.J Neurosci. 2016 Mar 9;36(10):3016-23. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2141-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26961955 Free PMC article.
-
The extrinsic modulation of hippocampal theta depends on the coactivation of cholinergic and GABA-ergic medial septal inputs.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1992 Fall;16(3):289-308. doi: 10.1016/s0149-7634(05)80203-9. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1992. PMID: 1528522 Review.
-
Speed and Oscillations: Medial Septum Integration of Attention and Navigation.Front Syst Neurosci. 2017 Sep 20;11:67. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2017.00067. eCollection 2017. Front Syst Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28979196 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Delay eyeblink conditioning performance and brain-wide c-Fos expression in male and female mice.Open Biol. 2023 May;13(5):220121. doi: 10.1098/rsob.220121. Epub 2023 May 10. Open Biol. 2023. PMID: 37161289 Free PMC article.
-
Theta- and gamma-band oscillatory uncoupling in the macaque hippocampus.Elife. 2023 May 4;12:e86548. doi: 10.7554/eLife.86548. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37139864 Free PMC article.
-
Disrupted working memory event-related network dynamics in multiple sclerosis.Commun Biol. 2024 Nov 29;7(1):1592. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07283-2. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39614100 Free PMC article.
-
Macroscale connections of the mouse lateral preoptic area and anterior lateral hypothalamic area.J Comp Neurol. 2022 Sep;530(13):2254-2285. doi: 10.1002/cne.25331. Epub 2022 May 17. J Comp Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35579973 Free PMC article.
-
Intersection of hippocampus and spinal cord: a focus on the hippocampal alpha-synuclein accumulation, dopaminergic receptors, neurogenesis, and cognitive function following spinal cord injury in male rats.BMC Neurosci. 2022 Jul 12;23(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12868-022-00729-5. BMC Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35820831 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

