Cannabidiol in Pharmacoresistant Epilepsy: Clinical Pharmacokinetic Data From an Expanded Access Program
- PMID: 33746760
- PMCID: PMC7966506
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.637801
Cannabidiol in Pharmacoresistant Epilepsy: Clinical Pharmacokinetic Data From an Expanded Access Program
Abstract
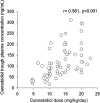
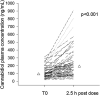
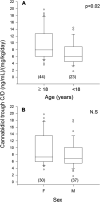
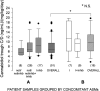
Background and Aim: Data on the clinical pharmacokinetics of cannabidiol (CBD) are scanty. We explored the effect of demographic and clinical variables on plasma concentrations of purified CBD in patients with Dravet (DS) and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS). Methods: The study design was an open, prospective, multicenter expanded access program (EAP). Venous blood samples were drawn from patients between 8 and 9 am, before the CBD morning dose, 12 h apart from the last evening dose, and then 2.5 h after their usual morning dose. Results: We collected 127 plasma samples (67-morning pre-dosing and 60 post-dosing) from 43 patients (24 females, 19 males), 27 with LGS and 16 with DS. Mean ± standard deviation age was 26 ± 15 years. Duration of CBD treatment averaged 4.2 ± 2.9 months at 13.2 ± 4.6 mg/kg/day. CBD median trough plasma concentration was 91 ng/ml; it doubled to 190 ng/ml 2.5 h post-dosing (p < 0.001). Cannabidiol trough plasma concentrations were linearly related to daily doses (r = 0.564, p < 0.001). Median trough CBD plasma concentration-to-weight-adjusted dose ratio (C/D) was 32% higher (p < 0.02) in plasma samples from subjects aged 18 and over than in those under 18. Sex and concomitant antiseizure medications (ASMs) were not associated with significant variations in CBD C/D, but caution is required due to the potential influence of confounders. Conclusion: These are the first data on CBD pharmacokinetics in children and adults with LGS or DS in a real-world setting. The most relevant finding was the higher CBD C/D in adults. In practice, reduced weight-normalized doses might be required with aging to achieve the same CBD plasma levels.
Keywords: Dravet syndrome; Lennox–Gastaut syndrome; antiseizure medication; cannabidiol; epilepsy; pharmacokinetics.
Copyright © 2021 Contin, Mohamed, Santucci, Lodi, Russo, Mecarelli and CBD LICE Italy Study Group.
Conflict of interest statement
OM has received consulting fees and speaker honoraria by Bial, Eisai, GW Pharmaceuticals, and UCB Pharma. ER has received speaker fees and/or fundings and has participated in advisory boards for Eisai, Pfizer, GW Pharmaceuticals, UCB Pharma, Arvelle Therapeutics. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Andrenyak D. M., Moody D. E., Slawson M. H., O’Leary D. S., Haney M. (2017). Determination of Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), 11-hydroxy-THC, 11-nor-9-carboxy-THC and cannabidiol in human plasma using gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Toxicol. 41, 277. 10.1093/jat/bkw136 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Crockett J., Critchley D., Tayo B., Berwaerts J., Morrison G. (2020). A phase 1, randomized, pharmacokinetic trial of the effect of different meal compositions, whole milk, and alcohol on cannabidiol exposure and safety in healthy subjects. Epilepsia 61, 267–277. 10.1111/epi.16419 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

