Electrophysiological Mechanisms Underlying T-Wave Alternans and Their Role in Arrhythmogenesis
- PMID: 33746768
- PMCID: PMC7969788
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.614946
Electrophysiological Mechanisms Underlying T-Wave Alternans and Their Role in Arrhythmogenesis
Abstract
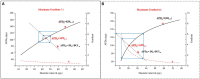
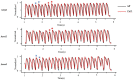
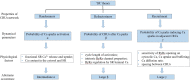
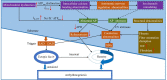
T-wave alternans (TWA) reflects every-other-beat alterations in the morphology of the electrocardiogram ST segment or T wave in the setting of a constant heart rate, hence, in the absence of heart rate variability. It is believed to be associated with the dispersion of repolarization and has been used as a non-invasive marker for predicting the risk of malignant cardiac arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death as numerous studies have shown. This review aims to provide up-to-date review on both experimental and simulation studies in elucidating possible mechanisms underlying the genesis of TWA at the cellular level, as well as the genesis of spatially concordant/discordant alternans at the tissue level, and their transition to cardiac arrhythmia. Recent progress and future perspectives in antiarrhythmic therapies associated with TWA are also discussed.
Keywords: T-wave alternans; arrhythmia; simulation; spatial discordant alternans; sudden cardiac death.
Copyright © 2021 You, Luo, Zhang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

