Early Growth and Protein-Energy Metabolism in Chicken Lines Divergently Selected on Ultimate pH
- PMID: 33746779
- PMCID: PMC7969813
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.643580
Early Growth and Protein-Energy Metabolism in Chicken Lines Divergently Selected on Ultimate pH
Abstract
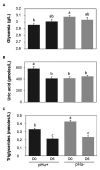
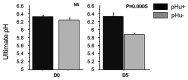
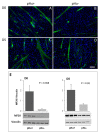
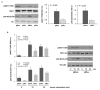
In chickens, a divergent selection on the Pectoralis major pHu allowed the creation of the pHu+ and pHu- lines, which represent a unique model for studying the biological control of carbohydrate storage in muscle. The present study aimed to describe the early mechanisms involved in the establishment of pHu+ and pHu- phenotypes. At hatching, pHu+ chicks were slightly heavier but exhibited lower plasma glucose and triglyceride and higher uric acid. After 5 days, pHu+ chicks exhibited higher breast meat yield compared to pHu- while their body weight was no different. At both ages, in vivo muscle glycogen content was lower in pHu+ than in pHu- muscles. The lower ability of pHu+ chicks to store carbohydrate in their muscle was associated with the increased expression of SLC2A1 and SLC2A3 genes coding glucose transporters 1 and 3, and of CS and LDHα coding key enzymes of oxidative and glycolytic pathways, respectively. Reduced muscle glycogen content at hatching of the pHu+ was concomitant with higher activation by phosphorylation of S6 kinase 1/ribosomal protein S6 pathway, known to activate protein synthesis in chicken muscle. In conclusion, differences observed in muscle at slaughter age in the pHu+ and pHu- lines are already present at hatching. They are associated with several changes related to both carbohydrate and protein metabolism, which are likely to affect their ability to use eggs or exogenous nutrients for muscle growth or energy storage.
Keywords: carbohydrate metabolism; chicks; glycogen; metabolism; muscle; protein synthesis.
Copyright © 2021 Métayer-Coustard, Tesseraud, Praud, Royer, Bordeau, Coudert, Cailleau-Audouin, Godet, Delaveau, Le Bihan-Duval and Berri.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Alnahhas N., Berri C., Boulay M., Baéza E., Jégo Y., Baumard Y., et al. (2014). Selecting broiler chickens for ultimate pH of breast muscle: analysis of divergent selection experiment and phenotypic consequences on meat quality, growth, and body composition traits. J. Anim. Sci. 92, 3816–3824. 10.2527/jas.2014-7597, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alnahhas N., Berri C., Chabault M., Chartrin P., Boulay M., Bourin M. C., et al. (2016). Genetic parameters of white striping in relation to body weight, carcass composition, and meat quality traits in two broiler lines divergently selected for the ultimate pH of the pectoralis major muscle. BMC Genet. 17:61. 10.1186/s12863-016-0369-2, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alnahhas N., Berri C., Chabault-Dhuit M., Bourin M., Arnould C., Le Bihan-Duval E. (2017). Combined effect of divergent selection for breast muscle ultimate pH and dietary amino acids on chicken performance, physical activity and meat quality. Animal 11, 335–344. 10.1017/S1751731116001580, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alnahhas N., Le Bihan-Duval E., Baéza E., Chabault M., Chartrin P., Bordeau T., et al. (2015). Impact of divergent selection for ultimate pH of pectoralis major muscle on biochemical, histological, and sensorial attributes of broiler meat. J. Anim. Sci. 93, 4524–4531. 10.2527/jas.2015-9100, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

